How can I help you?
Bind Data from SQL Server to Syncfusion® Blazor Components
19 Nov 202524 minutes to read
In this section, you can learn how to retrieve data from SQL database using Entity Framework to bind it to the Grid component and perform CRUD operations.
Entity Framework is an open-source object-relational mapper (O/RM) from Microsoft. Entity Framework works with many databases. But here, we are going to discuss the step-by-step procedure to create an Entity Framework using the MS SQL Server database and connect it to the Syncfusion® component to perform CRUD operations in a Blazor Server Application.
Prerequisite software
The following software are needed
- Visual Studio 2022
- .NET 6.0 or later.
- SQL Server 2019 or later
Create the database
The first step is to create a Library database and a table named Book to hold a list of books.
- Open SQL Server.
- Now, create a new database named Library.
- Right-click on the created database and select New Query.
- Use the following SQL query to create a table named Book.
Create Table Book(
Id BigInt Identity(1,1) Primary Key Not Null,
Name Varchar(200) Not Null,
Author Varchar(100) Not Null,
Quantity int,
Price int Not Null,
Available bit)
Now, the Book table design will look like below.
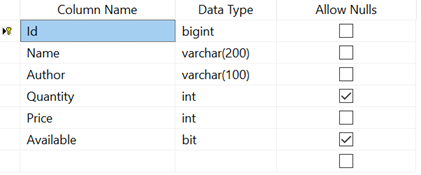
Creating Blazor Web App
Open Visual Studio and follow the steps in the documentation to create the Blazor Web App.
You need to configure the corresponding Interactive render mode and Interactivity location while creating a Blazor Web Application.
Create Blazor Server Application
Open Visual Studio 2022, select Create a New Project, select Blazor Server App, then click Next.
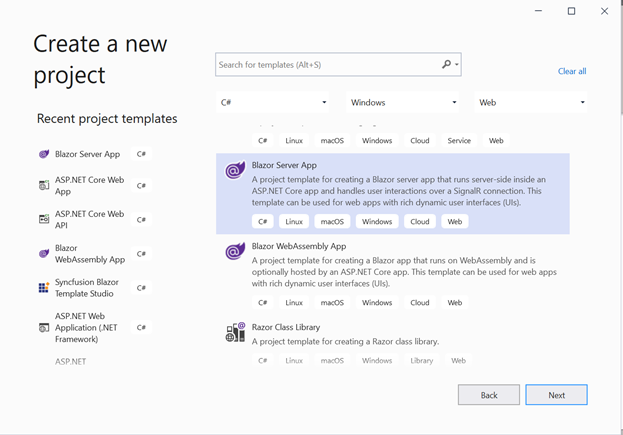
In the next window, provide the project name as LibraryManagement and click Next.
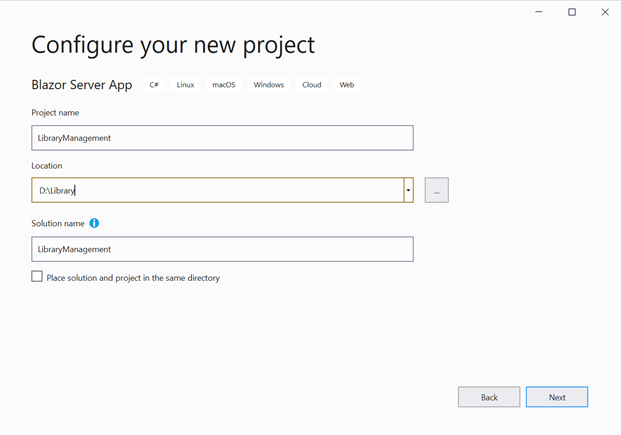
Now, select Target Framework as (.NET 6.0 or .NET 7.0) in the project template and click Create button to create the Blazor Server application.
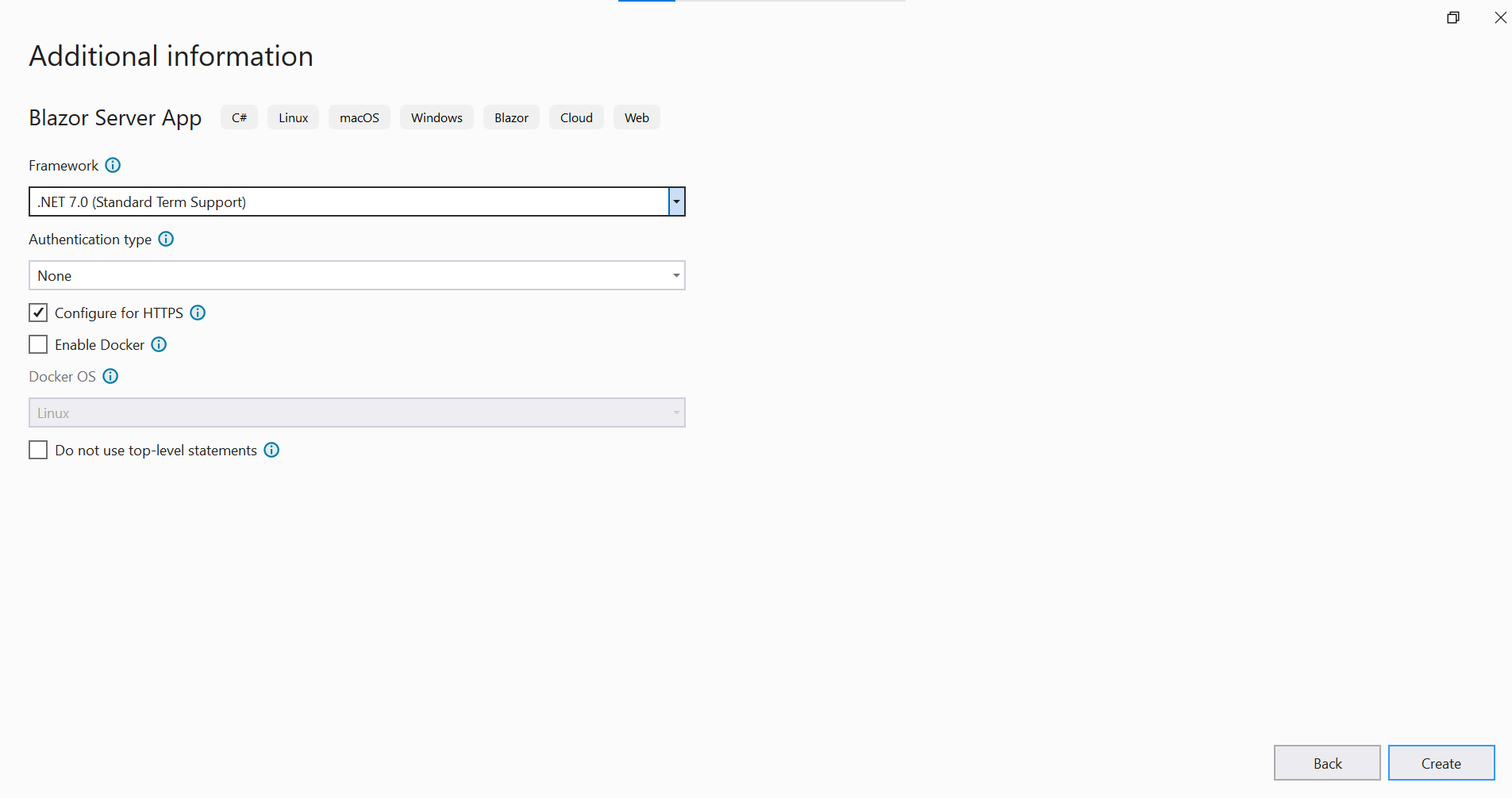
Creating DbContext and model class
DbContext and model class in Blazor Web App
Now, scaffold DbContext and model classes from the existing library database. To perform scaffolding and work with the SQL Server Database in our application, you need to install the following NuGet packages. If you have created a Blazor Web App with the interactive render mode set to WebAssembly or Auto, ensure to follow these steps:
- Create the new project with Class Library template named as
BlazorWebApp.Sharedfor DbContext and model class as shown below.
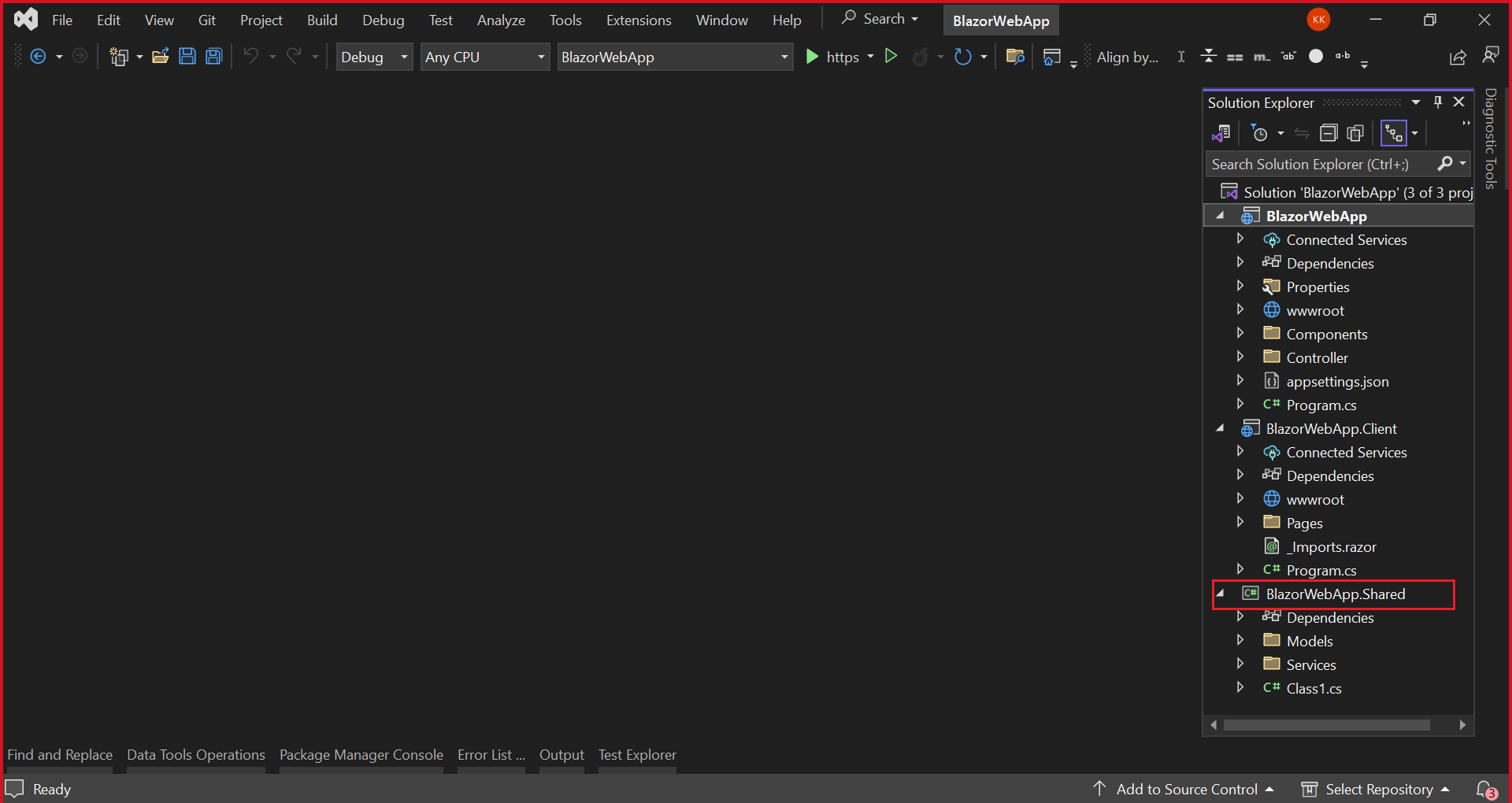
Additionally, ensure that you have added a reference to the BlazorWebApp.Shared project in both the server-side and client-side projects of your web application.
-
Then, open the NuGet Package Manager and install the following packages in both the shared and server-side projects of your app.
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools: This package creates database context and model classes from the database.
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer: The database provider that allows Entity Framework Core to work with SQL Server.
Alternatively, you can utilize the following package manager command to achieve the same.
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServerOnce the above packages are installed, you can scaffold DbContext and Model classes. Run the following command in the Package Manager Console under the BlazorWebApp.Shared project.
Scaffold-DbContext “Server=localhost;Database=Library;Integrated Security=True” Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -OutputDir Models
The above scaffolding command contains the following details for creating DbContext and model classes for the existing database and its tables.
- Connection string: Server=localhost;Database=Library;Integrated Security=True
- Data provider: Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
-
Output directory: -OutputDir Models
- After running the above command, LibraryContext.cs and Book.cs files will be created under the Models folder in the
BlazorWebApp.Sharedproject as follows.
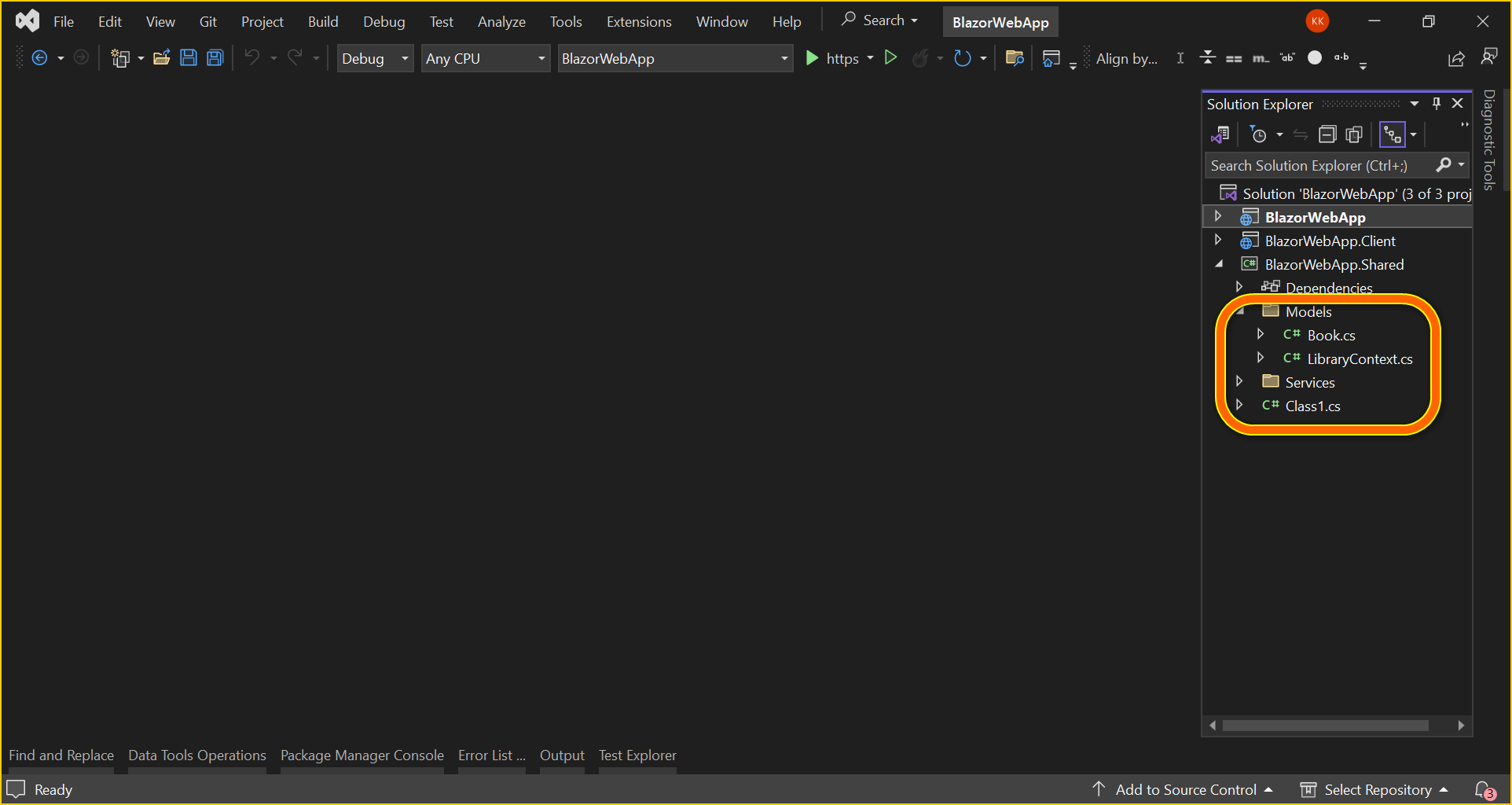
You can see that LibraryContext.cs file contains the connection string details in the OnConfiguring method.
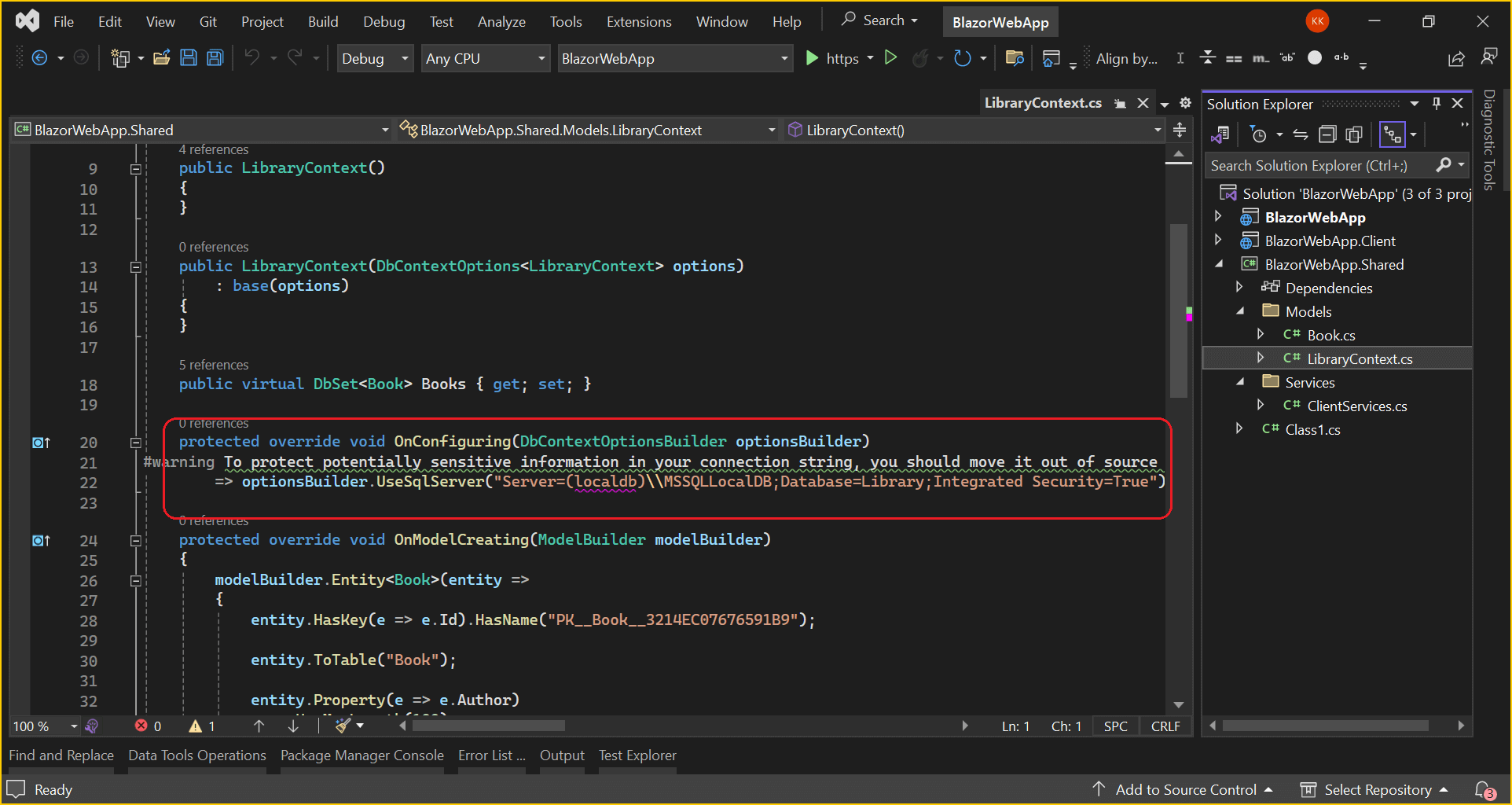
- Also, include the following code snippet in the app settings.json file from server side application.
// your localhost portal number
"BaseUri": "https://localhost:7105",
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"LibraryDatabase": "Server={Your server name};Database=Library;Integrated Security=True"
}
- Add the following code snippet to configure a scoped HttpClient with a base address and DbContext must be configured using connection string and registered as scoped service using the AddDbContext method in Program.cs file in server side application.
builder.Services.AddScoped(http => new HttpClient { BaseAddress = new Uri(builder.Configuration.GetSection("BaseUri").Value!) });
builder.Services.AddDbContext<LibraryContext>(option =>
option.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("LibraryDatabase")));
- Crete the
DataGridControllerin server side application for handle CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations for the Book entity.
using BlazorWebApp.Shared.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace BlazorWebApp.Controller
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class DataGridController : ControllerBase
{
public DataGridController ()
{
}
[HttpGet]
public async Task<ActionResult<List<Book>>> Get ()
{
LibraryContext db = new LibraryContext();
return db.Books.ToList();
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<ActionResult<Book>> Post ( Book value )
{
LibraryContext db = new LibraryContext();
db.Books.Add(value);
db.SaveChanges();
return Ok(value);
}
[HttpPut("{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<Book>> Put ( long id, Book updatedBook )
{
using (LibraryContext db = new LibraryContext())
{
var existingBook = await db.Books.FindAsync(id);
if (existingBook == null)
{
return NotFound(); // Return 404 Not Found if the book with the given id is not found
}
// Update the properties of the existing book with the values from the updated book
existingBook.Name = updatedBook.Name;
existingBook.Author = updatedBook.Author;
existingBook.Price = updatedBook.Price;
existingBook.Quantity = updatedBook.Quantity;
// Update other properties as needed
await db.SaveChangesAsync(); // Save changes to the database
return Ok(existingBook); // Return the updated book
}
}
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult> Delete ( long id )
{
LibraryContext db = new LibraryContext();
var book = db.Books.Find(id);
if (book == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
db.Books.Remove(book);
db.SaveChanges();
return NoContent();
}
}
}Also, make sure to include the AddControllers and MapControllers methods in the Program.cs file of your server-side application.
....
builder.Services.AddControllers();
....
app.MapControllers();
....- Create a
Servicesfolder in theBlazorWebApp.Sharedproject. Inside theServicesfolder, create the ClientServices class. This class will be responsible for interacting with the server-side API to perform operations such as retrieving books, inserting a new book, removing a book, and updating a book.
public class ClientServices
{
private readonly HttpClient _httpClient;
public ClientServices ( HttpClient httpClient )
{
_httpClient = httpClient;
}
public async Task<List<Book>> GetBooks ()
{
var result = await _httpClient.GetFromJsonAsync<List<Book>>("https://localhost:7105/api/DataGrid");
return result;
}
public async Task<Book> InsertBook ( Book value )
{
await _httpClient.PostAsJsonAsync<Book>($"https://localhost:7105/api/DataGrid/", value);
return value;
}
public async Task<bool> RemoveBook ( long bookId )
{
HttpResponseMessage response = await _httpClient.DeleteAsync($"https://localhost:7105/api/DataGrid/{bookId}");
return true;
}
public async Task<Book> UpdateBook ( long bookId, Book updatedBook )
{
HttpResponseMessage response = await _httpClient.PutAsJsonAsync($"https://localhost:7105/api/DataGrid/{bookId}", updatedBook);
return updatedBook;
}
}Additionally, make sure to register the ClientServices class in both Program.cs files of your application.
....
builder.Services.AddScoped<ClientServices>();
NOTE
To ensure the using correct your’s localhost portable number in code snippet.
DbContext and model class in Blazor Server App
Now, scaffold DbContext and model classes from the existing library database. To perform scaffolding and work with the SQL Server Database in our application, you need to install the following NuGet packages.
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools: This package creates database context and model classes from the database.
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer: The database provider that allows Entity Framework Core to work with SQL Server.
Run the following commands in the Package Manager Console.
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServerOnce the above packages are installed, you can scaffold DbContext and Model classes. Run the following command in the Package Manager Console under the LibraryManagement project.
Scaffold-DbContext “Server=localhost;Database=Library;Integrated Security=True” Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -OutputDir Models
The above scaffolding command contains the following details for creating DbContext and model classes for the existing database and its tables.
- Connection string: Server=localhost;Database=Library;Integrated Security=True
- Data provider: Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
- Output directory: -OutputDir Models
After running the above command, LibraryContext.cs and Book.cs files will be created under the LibraryManagement.Models folder as follows.
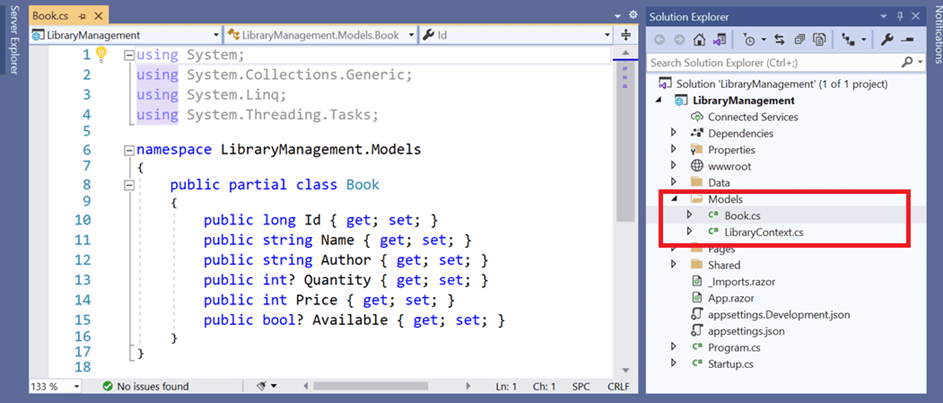
You can see that LibraryContext.cs file contains the connection string details in the OnConfiguring method.
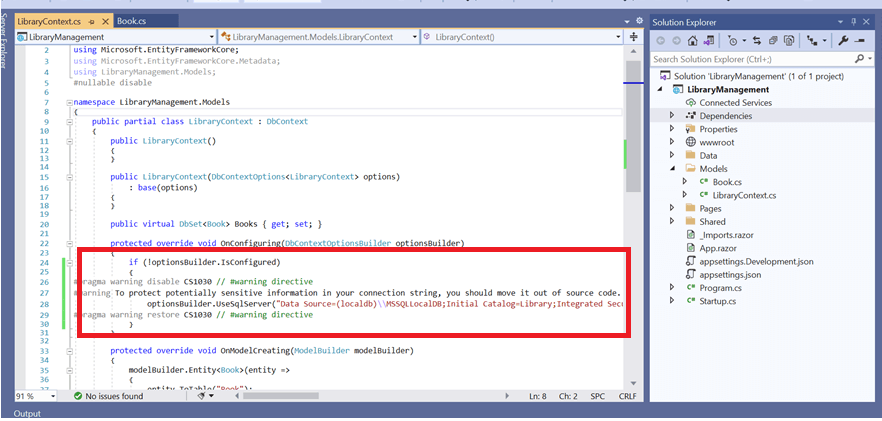
It is not recommended to have a connection string with sensitive information in the LibraryContext.cs file, so the connection string is moved to the app settings.json file.
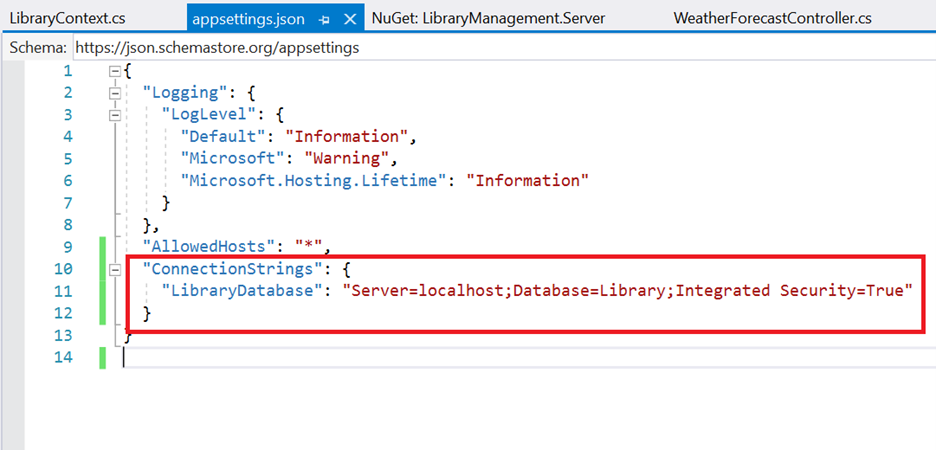
Now, the DbContext must be configured using connection string and registered as scoped service using the AddDbContext method in Program.cs file in .NET 6 and .NET 7 application.
builder.Services.AddDbContext<LibraryContext>(option =>
option.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("LibraryDatabase")));Creating a Data Access Layer
The application is now configured to connect with the library database using Entity Framework. Now, it’s time to consume data from the library database. To do so, you need an interface to fetch data from DbContext to the Blazor application.
To create an interface, right-click on the Models folder and create an interface called ILibraryService.cs like below.
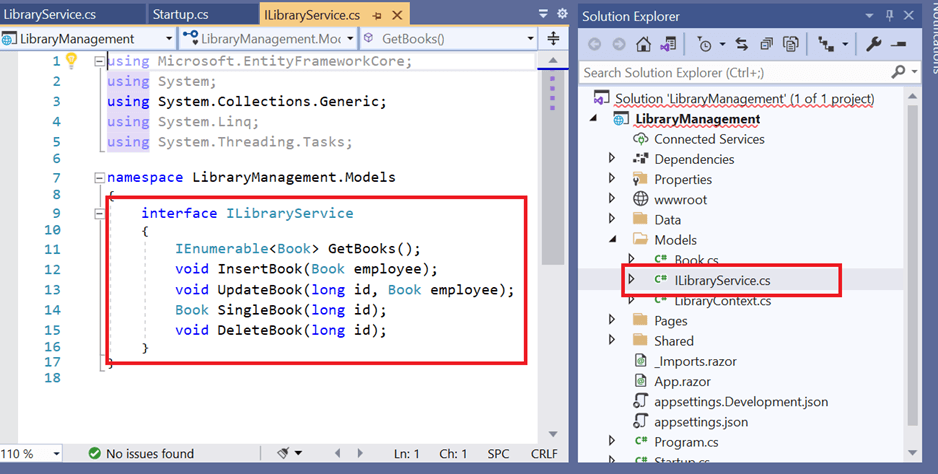
Create a data access layer LibraryService.cs.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace LibraryManagement.Models
{
public class LibraryService : ILibraryService
{
private LibraryContext _context;
public LibraryService(LibraryContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
public void DeleteBook(long id)
{
try
{
Book ord = _context.Books.Find(id);
_context.Books.Remove(ord);
_context.SaveChanges();
}
catch
{
throw;
}
}
public IEnumerable<Book> GetBooks()
{
try
{
return _context.Books.ToList();
}
catch
{
throw;
}
}
public void InsertBook(Book book)
{
try
{
_context.Books.Add(book);
_context.SaveChanges();
}
catch
{
throw;
}
}
public Book SingleBook(long id)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public void UpdateBook(long id, Book book)
{
try
{
var local = _context.Set<Book>().Local.FirstOrDefault(entry => entry.Id.Equals(book.Id));
// check if local is not null
if (local != null)
{
// detach
_context.Entry(local).State = EntityState.Detached;
}
_context.Entry(book).State = EntityState.Modified;
_context.SaveChanges();
}
catch
{
throw;
}
}
}
}Register the service in Program.cs
Now, you need to register the LibraryService and ILibraryService as services in the Program.cs file for .NET6 and .NET7 applications. Register the Scoped Services like below.
builder.Services.AddScoped<ILibraryService, LibraryService>();
builder.Services.AddDbContext<LibraryContext>(option =>
option.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("LibraryDatabase")));Add Syncfusion® Blazor Grid and Themes NuGet in Blazor App
To add Blazor DataGrid component in the app, open the NuGet package manager in Visual Studio (Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Manage NuGet Packages for Solution), search and install Syncfusion.Blazor.Grid and Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes.
If you utilize WebAssembly or Auto render modes in the Blazor Web App need to be install Syncfusion® Blazor components NuGet packages within the client project.
Alternatively, you can utilize the following package manager command to achieve the same.
Install-Package Syncfusion.Blazor.Grid -Version 32.2.3
Install-Package Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes -Version 32.2.3NOTE
Syncfusion® Blazor components are available in nuget.org. Refer to NuGet packages topic for available NuGet packages list with component details.
Open ~/_Imports.razor file and import the following namespace.
@using Syncfusion.Blazor
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.GridsNow, register the Syncfusion® Blazor Service in the ~/Program.cs file of your App.
For a Blazor Web App with WebAssembly or Auto (Server and WebAssembly) interactive render mode, register the Syncfusion® Blazor service in both ~/Program.cs files of your web app.
....
using Syncfusion.Blazor;
....
builder.Services.AddSyncfusionBlazor();
....Themes provide life to components. Syncfusion® Blazor has different themes. They are:
- Fabric
- Bootstrap
- Material
- High Contrast
In this demo application, the latest theme will be used.
-
For Blazor Web App, refer stylesheet inside the
<head>of ~/Components/App.razor file for .NET 10, .NET 9 and .NET 8. - For Blazor WebAssembly application, refer stylesheet inside the
<head>element of wwwroot/index.html file. - For Blazor Server application, refer stylesheet inside the
<head>element of- ~/Pages/_Host.cshtml file for .NET 7.
- ~/Pages/_Layout.cshtml file for .NET 6.
<link href="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />Also, Include the script reference at the end of the <body> of ~/Components/App.razor(For Blazor Web App) or Pages/_Host.cshtml (for Blazor Server App) file as shown below:
<body>
....
<script src="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Core/scripts/syncfusion-blazor.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</body>Add Syncfusion® Blazor DataGrid component to an application
In previous steps, you have successfully configured the Syncfusion® Blazor package in the application. Now, you can add the grid component to the .razor page inside the Pages folder.
If you have set the interactivity location to Per page/component in the web app, ensure that you define a render mode at the top of the Syncfusion® Blazor component-included razor page as follows:
@* Your App render mode define here *@
@rendermode InteractiveAuto<SfGrid TValue="Book">
</SfGrid>Bind data to Blazor DataGrid component using Entity Framework
To consume data from the database using Entity Framework, you need to inject the LibraryService into the razor page and assign it to the DataGrid’s datasource variable. Here, the DataSource property of the DataGrid component is used to bind the SQL data using Entity Framework in the Server-side application
@using BlazorWebApp.Shared.Models
@using BlazorWebApp.Shared.Services
<SfGrid DataSource="@LibraryBooks" TValue="Book">
</SfGrid>
@code
{
public List<Book> LibraryBooks { get; set; }
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync ()
{
LibraryBooks = await clientlibrary.GetBooks();
}
}@using LibraryManagement.Models
@inject ILibraryService LibraryService
<SfGrid DataSource="@LibraryBooks" TValue="Book">
</SfGrid>
@code
{
public IEnumerable<Book> LibraryBooks { get; set; }
protected override void OnInitialized()
{
LibraryBooks = LibraryService.GetBooks();
}
}Grid columns can be defined using the GridColumn component. We are going to create columns using the following code. Let us see the properties used and their usage.
- Field property specifies the column name of the Book table to display in the grid column.
- IsPrimaryKey property specifies that the given column is a primary key column. Here, Id column is a primary key column.
- Visible property specifies the column visibility. Setting as false will hide the column at the user end.
- Width property specifies the column width.
- Format property helps to format number, currencies, and date in a particular culture. Here, the Price column has been formatted.
- DisplayAsCheckBox property renders checkbox in cells and sets check state based on the property value. Here, Available column is rendered as a checkbox column.
@using BlazorWebApp.Shared.Models
@using BlazorWebApp.Shared.Services
<SfGrid DataSource="@LibraryBooks" TValue="Book">
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Id)" IsPrimaryKey="true" IsIdentity="true" Visible="false"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Name)" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Author)" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Quantity)" Width="90" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Price)" Width="90" Format="C2" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Available)" DisplayAsCheckBox="true" Width="70"></GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</SfGrid>
@code
{
public List<Book> LibraryBooks { get; set; }
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync ()
{
LibraryBooks = await clientlibrary.GetBooks();
}
}@using LibraryManagement.Models
@inject ILibraryService LibraryService
<SfGrid DataSource="@LibraryBooks" TValue="Book">
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Id)" IsPrimaryKey="true" IsIdentity="true" Visible="false"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Name)" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Author)" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Quantity)" Width="90" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Price)" Width="90" Format="C2" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Available)" DisplayAsCheckBox="true" Width="70"></GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</SfGrid>
@code
{
public IEnumerable<Book> LibraryBooks { get; set; }
protected override void OnInitialized()
{
LibraryBooks = LibraryService.GetBooks();
}
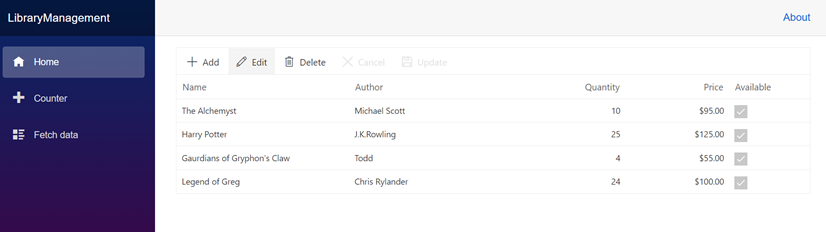
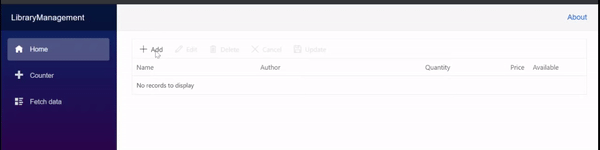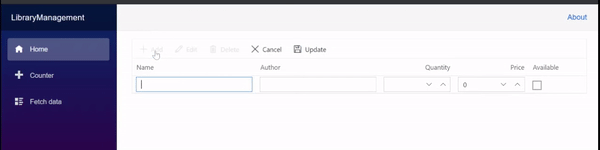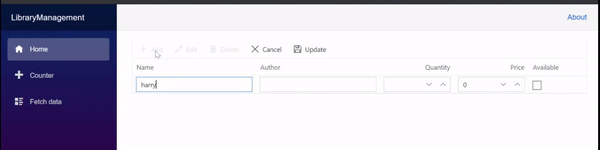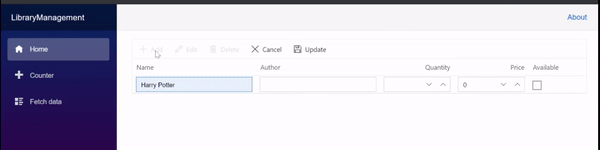
}Now, the data from the SQL server is loaded into the DataGrid component. Refer to the following screenshot for the output of above.
Handling CRUD operations with our Syncfusion® Blazor DataGrid component
You can enable editing in the grid component using the GridEditSettings component. Grid provides various modes of editing options such as Inline/Normal, Dialog, and Batch editing. Refer to the following documentation for your reference.
Here, inline edit mode and Toolbar property are used to show toolbar items for editing.
While using the DataSource property of Grid, changes will be reflected only in the Grid datasource. To reflect them in the database, handle the CRUD operations externally using the OnActionBegin and OnActionComplete events of Grid.
- OnActionBegin – This event will be triggered when the action gets initiated. So, while inserting/updating a record, RequestType Save will be sent in the event arguments to save the changes in the database. Similarly, while deleting a record, RequestType as Delete will be initiated to perform actions externally. Since for both Update and Insert action, RequestType will be Save, you can differentiate them by using the Args.Action property, which will indicate the current action.
- OnActionComplete – It will be triggered when certain actions are completed. Here, you can refresh the Grid component with an updated datasource to reflect the changes.
We have added the DataGrid editing, toolbar, and OnActionBegin and OnActionComplete event code with the previous Grid model.
@rendermode InteractiveAuto
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Data
@using BlazorWebApp.Shared.Models
@using BlazorWebApp.Shared.Services
@inject ClientServices clientlibrary
<SfGrid DataSource="@LibraryBooks" Toolbar="@(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Cancel", "Update" })" TValue="Book">
<GridEditSettings AllowAdding="true" AllowDeleting="true" AllowEditing="true" Mode="EditMode.Normal"></GridEditSettings>
<GridEvents OnActionBegin="ActionBeginHandler" OnActionComplete="ActionCompleteHandler" TValue="Book"></GridEvents>
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Id)" IsPrimaryKey="true" IsIdentity="true" Visible="false" ></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Name)" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Author)" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Quantity)" Width="90" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Price)" Width="90" Format="C2" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Available)" DisplayAsCheckBox="true" Width="70"></GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</SfGrid>
@code
{
public List<Book> LibraryBooks { get; set; }
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync ()
{
LibraryBooks = await clientlibrary.GetBooks();
}
public async void ActionBeginHandler ( ActionEventArgs<Book> Args )
{
//Will be triggered when CRUD action is initiated
}
public async void ActionCompleteHandler ( ActionEventArgs<Book> Args )
{
//will be triggered when CRUD action is complete.
if (Args.RequestType.Equals(Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids.Action.Save))
{
LibraryBooks = await clientlibrary.GetBooks(); //to fetch the updated data from db to Grid
}
}
}@using LibraryManagement.Models
@inject ILibraryService LibraryService
<SfGrid DataSource="@LibraryBooks" Toolbar="@(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Cancel", "Update" })" TValue="Book">
<GridEditSettings AllowAdding="true" AllowDeleting="true" AllowEditing="true" Mode="EditMode.Normal"></GridEditSettings>
<GridEvents OnActionBegin="ActionBeginHandler" OnActionComplete="ActionCompleteHandler" TValue="Book"></GridEvents>
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Id)" IsPrimaryKey="true" IsIdentity="true" Visible="false" ></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Name)" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Author)" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Quantity)" Width="90" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Price)" Width="90" Format="C2" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(Book.Available)" DisplayAsCheckBox="true" Width="70"></GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</SfGrid>
@code
{
public IEnumerable<Book> LibraryBooks { get; set; }
protected override void OnInitialized()
{
LibraryBooks = LibraryService.GetBooks();
}
public void ActionBeginHandler(ActionEventArgs<Book> Args)
{
//Will be triggered when CRUD action is initiated
}
public void ActionCompleteHandler(ActionEventArgs<Book> Args)
{
//will be triggered when CRUD action is complete.
if (Args.RequestType.Equals(Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids.Action.Save))
{
LibraryBooks = LibraryService.GetBooks(); //to fetch the updated data from db to Grid
}
}
}NOTE
Normal edit mode is the default mode of editing.
Insert a row
To insert a new row, click the Add toolbar button. The new record edit form will look like below.
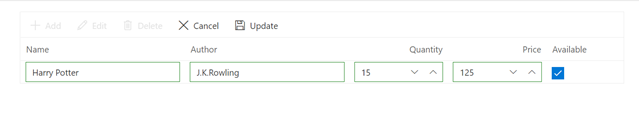
Clicking the Update toolbar button will initiate the insert action in Grid. Now, the OnActionBegin event will be triggered with a RequestType as Save. You can insert the record into the database (Book table) by calling the InsertBook() method of the ClientServices in Blazor Web App(BlazorWebApp.Shared project) and LibraryService in Blazor Server App.
public async void ActionBeginHandler ( ActionEventArgs<Book> Args )
{
//Will be triggered when CRUD action is initiated
if (Args.Action == "Add")
{
// Insert the changes into your database here.
await clientlibrary.InsertBook(Args.Data);
}
}public void ActionBeginHandler(ActionEventArgs<Book> Args)
{
if (Args.RequestType.Equals(Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids.Action.Save))
{
if (Args.Action == "Add")
{
// Insert the changes into your database here.
LibraryService.InsertBook(Args.Data);
}
}
}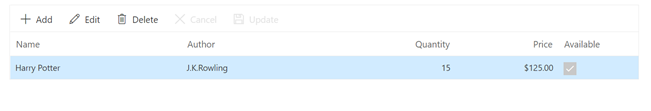
Update a row
To edit a row, select any row and click the Edit toolbar button. The edit form will look like below.
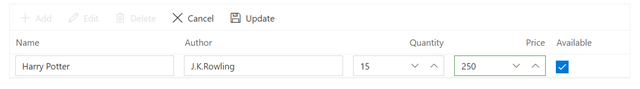
Now, the Price column value is changed to 125 from 250. Clicking the Update toolbar button will initiate the update action and trigger the OnActionBegin event with Save RequestType. Here, you can update the record in the Book table by calling the UpdateBook() method of the ClientServices in Blazor Web App(BlazorWebApp.Shared project) and LibraryService in Blazor Server App when Args.Action is Edit. Refer to the following code example.
public async void ActionBeginHandler ( ActionEventArgs<Book> Args )
{
if (Args.Action == "Edit")
{
//Update the changes into your database here.
await clientlibrary.UpdateBook(Args.Data.Id, Args.Data);
}
}public void ActionBeginHandler(ActionEventArgs<Book> Args)
{
if (Args.RequestType.Equals(Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids.Action.Save))
{
if (Args.Action == "Edit")
{
//Update the changes into your database here.
LibraryService.UpdateBook(Args.Data.Id, Args.Data);
}
}
}The resultant grid will look like below.
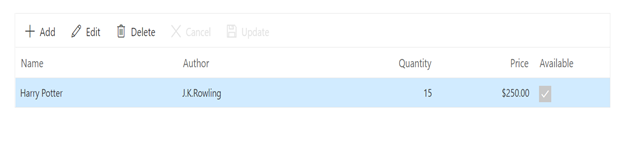
Delete a row
To delete a row, select any row and click the Delete toolbar button. Deleting operation will initiate the OnActionBegin event with RequestType as Delete. Now, you can delete the record from the database by calling DeleteBook() method of ClientServices in Blazor Web App(BlazorWebApp.Shared project) and LibraryService in Blazor Server App with the selected record`s primary key value. Refer to the following code example.
public void ActionBeginHandler(ActionEventArgs<Book> Args)
{
if (Args.RequestType.Equals(Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids.Action.Delete))
{
//Remove the record from your database
LibraryService.DeleteBook(Args.Data.Id);
}
}public async void ActionBeginHandler ( ActionEventArgs<Book> Args )
{
if (Args.RequestType.Equals(Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids.Action.Delete))
{
//Remove the record from your database
await clientlibrary.RemoveBook(Args.Data.Id);
}
}
NOTE
Find the sample from this Github location.