How can I help you?
Populate Data in Blazor Maps Component
4 Nov 202514 minutes to read
This section explains how to supply data inputs and provide them to the Maps component.
Geometry types
GeoJSON data contains geometry objects with properties such as geometry types and coordinates. Geometry types specify the shape to render, and coordinates define the shape’s boundary. The supported geometry types are:
| Shapes | Supported |
|---|---|
| Polygon | Yes |
| MultiPolygon | Yes |
| LineString | Yes |
| MultiLineString | Yes |
| Point | Yes |
| MultiPoint | Yes |
| GeometryCollection | Yes |
Shape data
The shape data collection describes geographic shape information in GeoJSON format. Map shapes are rendered from this data. Custom shapes, such as seat selections in a bus or a cricket stadium, can also be added as ShapeData in the MapsLayer.
Data source
The DataSource property represents statistical data for the Maps component and accepts a collection of values. For example, a list of objects can be provided. This data source is used to color shapes, display data labels, show tooltips, and more.
The data source is populated with a list of objects related to the shape data. In the following example, PopulationDetails is used as the data source for Maps.
@code{
public class PopulationDetail
{
public string Code { get; set; }
public double Value { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Population { get; set; }
public double Density { get; set; }
};
private List<PopulationDetail> PopulationDetails = new List<PopulationDetail> {
new PopulationDetail {
Code = "AF",
Value= 53,
Name= "Afghanistan",
Population= 29863010,
Density= 119
},
new PopulationDetail {
Code= "AL",
Value= 117,
Name= "Albania",
Population= 3195000,
Density= 111
},
new PopulationDetail {
Code= "DZ",
Value= 15,
Name= "Algeria",
Population= 34895000,
Density= 15
}
};
}Data binding
The following properties in the MapsLayer are used to bind data in the Maps component. These properties work together.
- ShapePropertyPath
- ShapeDataPath
ShapePropertyPath
The ShapePropertyPath property refers to the field name in the ShapeData of shape layers used to identify a shape. When the values of ShapeDataPath property from the DataSource and ShapePropertyPath property from the ShapeData match, the associated object from the data source is bound to the corresponding shape.
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Maps
<SfMaps>
<MapsLayers>
<MapsLayer ShapeData='new {dataOptions= "https://cdn.syncfusion.com/maps/map-data/world-map.json"}'
ShapePropertyPath='new string[] {"name"}' TValue="string">
</MapsLayer>
</MapsLayers>
</SfMaps>NOTE
The
world-map.jsonfile contains the following data, and the name field value is used to map the corresponding shape with the provided data source.
[
{
"type": "Feature",
"properties": {
"admin": "Afghanistan",
"name": "Afghanistan",
"continent": "Asia"
},
"geometry": { "type": "Polygon", "coordinates": [[[61.21081709172573, ...
},
...
]ShapeDataPath
The ShapeDataPath property is similar to ShapePropertyPath, but it refers to the field name in the DataSource. In the following population data, the fields are Name, Population, and Density. The Name field is set to ShapeDataPath property to map the corresponding value of the field name in shape data.
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Maps
<SfMaps>
<MapsLayers>
<MapsLayer ShapeData='new {dataOptions= "https://cdn.syncfusion.com/maps/map-data/world-map.json"}'
DataSource="PopulationDetails" ShapePropertyPath='new string[] {"name"}'
ShapeDataPath="Name" TValue="PopulationDetail">
</MapsLayer>
</MapsLayers>
</SfMaps>
@code{
public class PopulationDetail
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Population { get; set; }
public double Density { get; set; }
};
private List<PopulationDetail> PopulationDetails = new List<PopulationDetail> {
new PopulationDetail {
Name= "Afghanistan",
Population= 29863010,
Density= 119
},
...
};
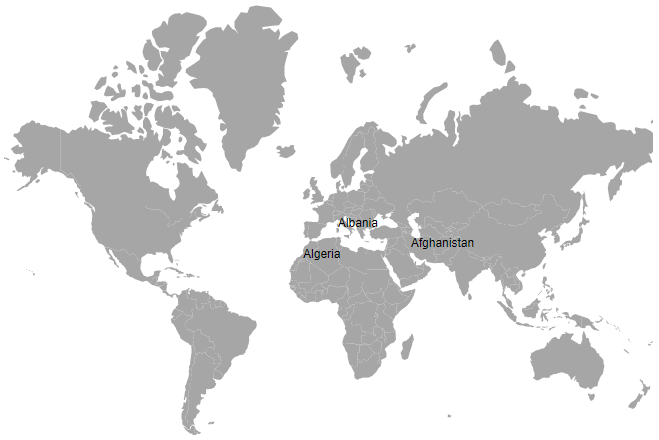
}In the above example, both name fields contain the value Afghanistan. This value is matched in both shape data and the data source, so the details associated with Afghanistan are mapped to the corresponding shape and used to color the shape, display data labels, and display tooltips.
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Maps
<SfMaps>
<MapsLayers>
<MapsLayer ShapeData='new {dataOptions= "https://cdn.syncfusion.com/maps/map-data/world-map.json"}'
DataSource="PopulationDetails"
ShapeDataPath="Name"
ShapePropertyPath='new string[] {"name"}' TValue="PopulationDetail">
@* It display data label for bounded items *@
<MapsDataLabelSettings Visible="true" LabelPath="Name"></MapsDataLabelSettings>
</MapsLayer>
</MapsLayers>
</SfMaps>
@code {
public class PopulationDetail
{
public string Code { get; set; }
public double Value { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Population { get; set; }
public double Density { get; set; }
};
private List<PopulationDetail> PopulationDetails = new List<PopulationDetail> {
new PopulationDetail {
Code = "AF",
Value= 53,
Name= "Afghanistan",
Population= 29863010,
Density= 119
},
new PopulationDetail {
Code= "AL",
Value= 117,
Name= "Albania",
Population= 3195000,
Density= 111
},
new PopulationDetail {
Code= "DZ",
Value= 15,
Name= "Algeria",
Population= 34895000,
Density= 15
}
};
}
Fetching data from JSON file
To retrieve data from a JSON file, create a Blazor WebAssembly app or a Blazor Server app. Read the data from the JSON file, convert it to a C# object, and assign it to the DataSource property.
Fetching data from JSON file using Blazor WebAssembly App
The Http.GetFromJsonAsync method is used in the OnInitializedAsync lifecycle method to load JSON data. Because this executes asynchronously, check whether PopulationDensity is available; then render the Maps component or display a loading message.
@inject HttpClient Http;
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Maps
@inject NavigationManager NavigationManager
@if (PopulationDensity == null)
{
<p><em>Loading Maps component...</em></p>
}
else
{
<SfMaps>
<MapsLayers>
<MapsLayer ShapeData='new {dataOptions ="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/maps/map-data/world-map.json"}'
DataSource="PopulationDensity"
ShapeDataPath="Name"
ShapePropertyPath='new string[] {"name"}' TValue="PopulationData">
<MapsDataLabelSettings Visible="true" LabelPath="Name"></MapsDataLabelSettings>
</MapsLayer>
</MapsLayers>
</SfMaps>
}
@code {
PopulationData[] PopulationDensity;
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
PopulationDensity = await Http.GetFromJsonAsync<PopulationData[]>(NavigationManager.Uri + "sample-data/PopulationDensity.json");
}
public class PopulationData
{
public string Code { get; set; }
public double Value { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Population { get; set; }
public float Density { get; set; }
}
}Here, the PopulationDensity.json file contains the following data.
[
{
"code": "AF",
"value": 53,
"name": "Afghanistan",
"population": 29863010,
"density": 119
},
{
"code": "AL",
"value": 117,
"name": "Albania",
"population": 3195000,
"density": 111
},
{
"code": "DZ",
"value": 15,
"name": "Algeria",
"population": 34895000,
"density": 15
}
]
Fetching data from JSON file using Blazor Server App
The Http.GetAsync method is used in the OnInitializedAsync lifecycle method to get the JSON file as a response and read it as a string. Then, the JSON data is deserialized to a list of objects and assigned to the DataSource property of the Maps component. Because this executes asynchronously, check whether PopulationDensity is available; then render the Maps component or display a loading message.
@inject HttpClient Http;
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Maps
@using System.Net.Http.Json
@using System.Text.Json;
@using Newtonsoft.Json;
@inject NavigationManager NavigationManager
@if (PopulationDensity == null)
{
<p><em>Loading Maps component...</em></p>
}
else
{
<SfMaps>
<MapsLayers>
<MapsLayer ShapeData='new {dataOptions ="https://cdn.syncfusion.com/maps/map-data/world-map.json"}'
DataSource="PopulationDensity"
ShapeDataPath="Name"
ShapePropertyPath='new string[] {"name"}' TValue="PopulationData">
<MapsDataLabelSettings Visible="true" LabelPath="Name"></MapsDataLabelSettings>
</MapsLayer>
</MapsLayers>
</SfMaps>
}
@code {
public List<PopulationData> PopulationDensity;
public string result;
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
string path = NavigationManager.Uri + "sample-data/PopulationDensity.json";
HttpClient httpClient = new HttpClient();
HttpResponseMessage response = await Http.GetAsync(path);
result = response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result;
PopulationDensity = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<List<PopulationData>>(result);
}
public class PopulationData
{
public string Code { get; set; }
public double Value { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Population { get; set; }
public float Density { get; set; }
}
}