How can I help you?
File Source in Blazor File Upload Component
4 Nov 20259 minutes to read
Directory upload
The Blazor File Upload component can upload all files within a selected folder (including subfolders) to the server by enabling the DirectoryUpload property. When enabled, the Uploader iterates through files and subdirectories in the chosen folder and queues them for upload. The folder picker is shown instead of a file picker, allowing selection of folders only.
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Inputs
<SfUploader ID="UploadFiles" AutoUpload=false DirectoryUpload=true>
<UploaderAsyncSettings SaveUrl="api/SampleData/Save" RemoveUrl="api/SampleData/Remove"></UploaderAsyncSettings>
</SfUploader>Save action configuration in server-side blazor
The uploader save action configuration in a server-side Blazor application using MVC via UseMvcWithDefaultRoute in ASP.NET Core 3.0 and services.AddMvc(option => option.EnableEndpointRouting = false).SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_3_0) on IServiceCollection requires an explicit opt-in inside the Startup.cs file. This is necessary so MVC can determine whether to rely on authorization and CORS middleware during initialization.
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc(option => option.EnableEndpointRouting = false).SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_3_0);
services.AddRazorPages();
services.AddServerSideBlazor();
services.AddSingleton<WeatherForecastService>();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseMvcWithDefaultRoute();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapBlazorHub<App>(selector: "app");
endpoints.MapFallbackToPage("/_Host");
});
}Server-side configuration for save the files of folders
The following example demonstrates receiving uploaded files from selected folders and creating corresponding directories before saving files. In production, validate and sanitize path segments to prevent path traversal, and write to a dedicated uploads directory with appropriate permissions.
private IHostingEnvironment hostingEnv;
public SampleDataController(IHostingEnvironment env)
{
this.hostingEnv = env;
}
[HttpPost("[action]")]
public void Save(IList<IFormFile> chunkFile, IList<IFormFile> UploadFiles)
{
long size = 0;
try
{
foreach (var file in UploadFiles)
{
var filename = ContentDispositionHeaderValue
.Parse(file.ContentDisposition)
.FileName
.Trim('"');
var folders = filename.Split('/');
var uploaderFilePath = hostingEnv.ContentRootPath;
// for Directory upload
if (folders.Length > 1)
{
for (var i = 0; i < folders.Length - 1; i++)
{
var newFolder = uploaderFilePath + $@"\{folders[i]}";
Directory.CreateDirectory(newFolder);
uploaderFilePath = newFolder;
filename = folders[i + 1];
}
}
filename = uploaderFilePath + $@"\{filename}";
size += file.Length;
if (!System.IO.File.Exists(filename))
{
using (FileStream fs = System.IO.File.Create(filename))
{
file.CopyTo(fs);
fs.Flush();
}
}
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Response.Clear();
Response.StatusCode = 204;
Response.HttpContext.Features.Get<IHttpResponseFeature>().ReasonPhrase = "File failed to upload";
Response.HttpContext.Features.Get<IHttpResponseFeature>().ReasonPhrase = e.Message;
}
}
[HttpPost("[action]")]
public void Remove(IList<IFormFile> UploadFiles)
{
try
{
var filename = hostingEnv.ContentRootPath + $@"\{UploadFiles[0].FileName}";
if (System.IO.File.Exists(filename))
{
System.IO.File.Delete(filename);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Response.Clear();
Response.StatusCode = 200;
Response.HttpContext.Features.Get<IHttpResponseFeature>().ReasonPhrase = "File removed successfully";
Response.HttpContext.Features.Get<IHttpResponseFeature>().ReasonPhrase = e.Message;
}
}Drag and drop
The Uploader component supports drag-and-drop to add files to the upload queue. Drag files from the file explorer and drop them onto the drop area. By default, the Uploader acts as its own drop area and highlights the drop zone when files are dragged over it. Keyboard users can still browse using the built-in button.
Custom drop area
The Uploader can target an external element as the drop zone using the DropArea property. The target can be specified as an HTML element or by element ID. This replaces the default drop zone and visually confines drop interactions to the specified area.
SaveUrl and RemoveUrl actions are explained in this link.
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Inputs
<div ID="DropArea">
Drop files here to upload
</div>
<SfUploader ID="UploadFiles" AutoUpload=false DropArea="#DropArea">
<UploaderAsyncSettings SaveUrl="api/SampleData/Save" RemoveUrl="api/SampleData/Remove"></UploaderAsyncSettings>
</SfUploader>
<style>
#DropArea {
padding: 50px 25px;
margin: 30px auto;
border: 1px solid #c3c3c3;
text-align: center;
width: 20%;
display: inline-flex;
}
.e-file-select,
.e-file-drop {
display: none;
}
body .e-upload-drag-hover {
outline: 2px dashed brown;
}
#uploadfile {
width: 60%;
display: inline-flex;
margin-left: 5%;
}
</style>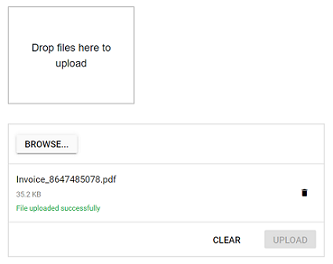
NOTE
You can also explore our Blazor File Upload example to understand how to browse the files that need to be uploaded to the server.