How can I help you?
WebApiAdaptor in Syncfusion® Blazor DataGrid
15 Sep 202524 minutes to read
The WebApiAdaptor is an extension of the ODataAdaptor, designed to interact with Web APIs created with OData endpoints. This adaptor ensures seamless communication between the Syncfusion® Blazor DataGrid and OData-endpoint-based Web APIs, enabling efficient data retrieval and manipulation. For successful integration, the endpoint must be capable of understanding OData-formatted queries sent along with the request.
To enable the OData query option for a Web API, please refer to the corresponding documentation, which provides detailed instructions on configuring the endpoint to understand OData-formatted queries.
This section describes a step-by-step process for retrieving data using the WebApiAdaptor and binding it to the Blazor Grid to facilitate data and CRUD operations.
Creating an API service
To configure a server with the Syncfusion® Blazor DataGrid, follow these steps:
1. Create a Blazor web app
You can create a Blazor Web App named WebApiAdaptor using Visual Studio 2022, either via Microsoft Templates or the Syncfusion® Blazor Extension. Make sure to configure the appropriate interactive render mode and interactivity location.
2. Create a model class
Create a new folder named Models. Then, add a model class named OrdersDetails.cs in the Models folder to represent the order data.
namespace WebApiAdaptor.Models
{
public class OrdersDetails
{
public static List<OrdersDetails> order = new List<OrdersDetails>();
public OrdersDetails() { }
public OrdersDetails(int OrderID, string CustomerId, int EmployeeId, double Freight, bool Verified, DateTime OrderDate, string ShipCity, string ShipName, string ShipCountry, DateTime ShippedDate, string ShipAddress)
{
this.OrderID = OrderID;
this.CustomerID = CustomerId;
this.EmployeeID = EmployeeId;
this.Freight = Freight;
this.ShipCity = ShipCity;
this.Verified = Verified;
this.OrderDate = OrderDate;
this.ShipName = ShipName;
this.ShipCountry = ShipCountry;
this.ShippedDate = ShippedDate;
this.ShipAddress = ShipAddress;
}
public static List<OrdersDetails> GetAllRecords()
{
if (order.Count() == 0)
{
int code = 10000;
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 1, "ALFKI", i + 0, 2.3 * i, false, new DateTime(1991, 05, 15), "Berlin", "Simons bistro", "Denmark", new DateTime(1996, 7, 16), "Kirchgasse 6"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 2, "ANATR", i + 2, 3.3 * i, true, new DateTime(1990, 04, 04), "Madrid", "Queen Cozinha", "Brazil", new DateTime(1996, 9, 11), "Avda. Azteca 123"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 3, "ANTON", i + 1, 4.3 * i, true, new DateTime(1957, 11, 30), "Cholchester", "Frankenversand", "Germany", new DateTime(1996, 10, 7), "Carrera 52 con Ave. Bolívar #65-98 Llano Largo"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 4, "BLONP", i + 3, 5.3 * i, false, new DateTime(1930, 10, 22), "Marseille", "Ernst Handel", "Austria", new DateTime(1996, 12, 30), "Magazinweg 7"));
order.Add(new OrdersDetails(code + 5, "BOLID", i + 4, 6.3 * i, true, new DateTime(1953, 02, 18), "Tsawassen", "Hanari Carnes", "Switzerland", new DateTime(1997, 12, 3), "1029 - 12th Ave. S."));
code += 5;
}
}
return order;
}
public int? OrderID { get; set; }
public string? CustomerID { get; set; }
public int? EmployeeID { get; set; }
public double? Freight { get; set; }
public string? ShipCity { get; set; }
public bool? Verified { get; set; }
public DateTime OrderDate { get; set; }
public string? ShipName { get; set; }
public string? ShipCountry { get; set; }
public DateTime ShippedDate { get; set; }
public string? ShipAddress { get; set; }
}
}3. Create an API controller
Create a new folder named Controllers. Then, add a controller named GridController.cs in the Controllers folder to handle data communication with Blazor DataGrid. Implement the Get method in the controller to return data in JSON format, including the Items and Count properties as required by the WebApiAdaptor.
The sample response object should look like this:
{
Items: [{..}, {..}, {..}, ...],
Count: 830
}
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Syncfusion.Blazor.Data;
using Syncfusion.Blazor;
using WebApiAdaptor.Models;
namespace WebApiAdaptor.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
public class GridController : ControllerBase
{
/// <summary>
/// Retrieve data from the data source.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object with the list of orders and the total count.</returns>
[HttpGet]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public object GetOrderData()
{
// Retrieve all order records.
List<OrdersDetails> data = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().ToList();
// Return the data and total count.
return new { Items = data, Count = data.Count() };
}
}
}When using the WebAPI Adaptor, the data source is returned as a pair of Items and Count. However, if the
Offlineproperty ofSfDataManageris enabled, the entire data source is returned from the server as a collection of objects. In this case, the$inlinecountwill not be included. Additionally, only a single request is made to fetch all the data from the server, and no further requests are sent.
4. Register controllers in Program.cs
Add the following lines in the Program.cs file to register controllers:
// Register controllers in the service container.
builder.Services.AddControllers();
// Map controller routes.
app.MapControllers();5. Run the application
Run the application in Visual Studio. The API will be accessible at a URL like https://localhost:xxxx/api/Grid (where xxxx represents the port number). Please verify that the API returns the order data.

Connecting Syncfusion® Blazor DataGrid to an API service
To integrate the Syncfusion® Blazor DataGrid into your project using Visual Studio, follow the below steps:
1. Install Syncfusion® Blazor DataGrid and Themes NuGet packages
To add the Blazor DataGrid in the app, open the NuGet Package Manager in Visual Studio (Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Manage NuGet Packages for Solution), search and install Syncfusion.Blazor.Grid and Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes.
If your Blazor Web App uses WebAssembly or Auto render modes, install the Syncfusion® Blazor NuGet packages in the client project.
Alternatively, use the following Package Manager commands:
Install-Package Syncfusion.Blazor.Grid -Version 32.2.3
Install-Package Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes -Version 32.2.3Syncfusion® Blazor components are available on nuget.org. Refer to the NuGet packages topic for a complete list of available packages.
2. Register Syncfusion® Blazor service
- Open the ~/_Imports.razor file and import the required namespaces.
@using Syncfusion.Blazor
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Data- Register the Syncfusion® Blazor service in the ~/Program.cs file.
using Syncfusion.Blazor;
builder.Services.AddSyncfusionBlazor();For apps using WebAssembly or Auto (Server and WebAssembly) render modes, register the service in both ~/Program.cs files.
3. Add stylesheet and script resources
Include the theme stylesheet and script references in the ~/Components/App.razor file.
<head>
....
<link href="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
....
<body>
....
<script src="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Core/scripts/syncfusion-blazor.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</body>
- Refer to the Blazor Themes topic for various methods to include themes (e.g., Static Web Assets, CDN, or CRG).
- Set the render mode to InteractiveServer or InteractiveAuto in your Blazor Web App configuration.
4. Add Blazor DataGrid and configure with server
To connect the Blazor DataGrid to a hosted API, use the Url property of SfDataManager. The SfDataManager offers multiple adaptor options to connect with remote database based on an API service. Below is an example of the WebApiAdaptor configuration where an API service are set up to return the resulting data in the Items and Count format. Update the Index.razor file as follows.
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Data
@using Syncfusion.Blazor
<SfGrid TValue="OrdersDetails" Height="348">
<SfDataManager Url="https://localhost:xxxx/api/Grid" Adaptor="Adaptors.WebApiAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field="OrderID" HeaderText="Order ID" Width="120" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="CustomerID" HeaderText="Customer Name" Width="160"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="ShipCity" HeaderText="Ship City" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="ShipCountry" HeaderText="Ship Country" Width="150"></GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</SfGrid>using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Syncfusion.Blazor.Data;
using Syncfusion.Blazor;
using WebApiAdaptor.Models;
namespace WebApiAdaptor.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
public class GridController : ControllerBase
{
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves order data.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object with the list of orders and the total count.</returns>
[HttpGet]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public object GetOrderData()
{
// Retrieve all order records.
List<OrdersDetails> data = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().ToList();
// Return the data and total count.
return new { Items = data, Count = data.Count() };
}
}
}Replace https://localhost:xxxx/api/Grid with the actual URL of your API endpoint that provides the data in a consumable format (e.g., JSON).
5. Run the application
When you run the application, the Blazor Grid will display data fetched from the API.
Perform data operations in a WebAPI service
When using the WebApiAdaptor with the SfDataManager, data operations such as filtering, sorting, paging, and searching are executed on the server side. These operations are sent from the client to the server as QueryString parameters, which can be accessed in your API controller using Request.Query.
Query parameters for data operations
The following table lists the query parameters used by the Blazor DataGrid for various data operations:
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
$skip, $top
|
Specifies the query parameters for performing paging operations on the server side. |
$filter |
Specifies the query parameter for performing filtering and searching operations on the server side. |
$orderby |
Specifies the query parameter for performing sorting operations on the server side. |
These parameters are automatically sent when the
WebApiAdaptoris used. You can access and process them in your Web API Controller to perform the corresponding operations.
Handling search operations
When a search operation is triggered, the $filter parameter is sent to the server. The $filter parameter specifies the query conditions that are applied to the data to perform the search.
The following example demonstrates how to extract the $filter parameter and apply search logic across multiple fields:
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves order data and handles search operations based on the provided filter query.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object containing the searched list of orders and the total count.</returns>
[HttpGet]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public object GetOrderData()
{
// Retrieve all order records from the data source.
List<OrdersDetails> data = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().ToList();
// Extract the query string from the incoming request.
var queryString = Request.Query;
// Enable nullable reference types for handling filter queries.
#nullable enable
string? filterQuery = queryString["$filter"];
#nullable disable
// Check if a filter query is provided.
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(filterQuery))
{
// Split the filter query into individual conditions using "and" as a delimiter.
var filterConditions = filterQuery.Split(new[] { " and " }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
foreach (var condition in filterConditions)
{
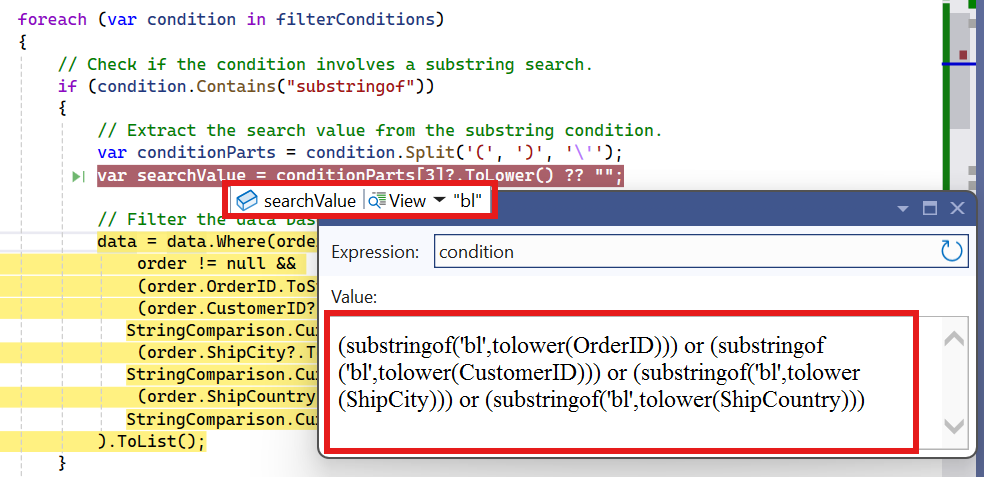
// Check if the condition involves a substring search.
if (condition.Contains("substringof"))
{
// Extract the search value from the substring condition.
var conditionParts = condition.Split('(', ')', '\'');
var searchValue = conditionParts[3]?.ToLower() ?? "";
// Filter the data based on the search value across multiple fields.
data = data.Where(order =>
order != null &&
(order.OrderID.ToString().Contains(searchValue) ||
(order.CustomerID?.ToLower().Contains(searchValue, StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase) ?? false) ||
(order.ShipCity?.ToLower().Contains(searchValue, StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase) ?? false) ||
(order.ShipCountry?.ToLower().Contains(searchValue, StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase) ?? false))
).ToList();
}
else
{
// Handle other filtering operations here.
}
}
}
// Calculate the total count of records.
int totalRecordsCount = data.Count();
// Return the filtered data and the total count as a JSON object.
return new { Items = data, count = totalRecordsCount };
}@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Data
@using Syncfusion.Blazor
<SfGrid TValue="OrdersDetails" Toolbar="@(new List<string>() { "Search" })" Height="348">
<SfDataManager Url="https://localhost:xxxx/api/Grid" Adaptor="Adaptors.WebApiAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field="OrderID" HeaderText="Order ID" Width="120" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="CustomerID" HeaderText="Customer Name" Width="160"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="ShipCity" HeaderText="Ship City" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="ShipCountry" HeaderText="Ship Country" Width="150"></GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</SfGrid>This example demonstrates a custom way of handling the
$filterquery sent by the Grid. You can also handle it using your own logic based on the query string format or use dynamic expression evaluation libraries for a more generic approach..
Handling filtering operation
When filtering is applied, the $filter parameter is sent to the server. The $filter parameter specifies the conditions for filtering the data based on the provided criteria.
The following example demonstrates how to extract the $filter parameter and apply filtering logic based on custom conditions:
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves order data and processes filtering operations based on the provided query parameters.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object containing the filtered list of orders and the total count.</returns>
[HttpGet]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public object GetOrderData()
{
// Retrieve all order records from the data source.
List<OrdersDetails> data = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().ToList();
// Extract the query string from the incoming request.
var queryString = Request.Query;
// Enable nullable reference types for handling filter queries.
#nullable enable
string? filterQuery = queryString["$filter"];
#nullable disable
// Check if a filter query is provided.
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(filterQuery))
{
// Split the filter query into individual conditions using "and" as a delimiter.
var filterConditions = filterQuery.Split(new[] { " and " }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
foreach (var condition in filterConditions)
{
// Check if the condition involves a substring search.
if (condition.Contains("substringof"))
{
// Handle substring search operation here.
}
else
{
// Initialize variables to hold the filter field and value.
string filterField = "";
string filterValue = "";
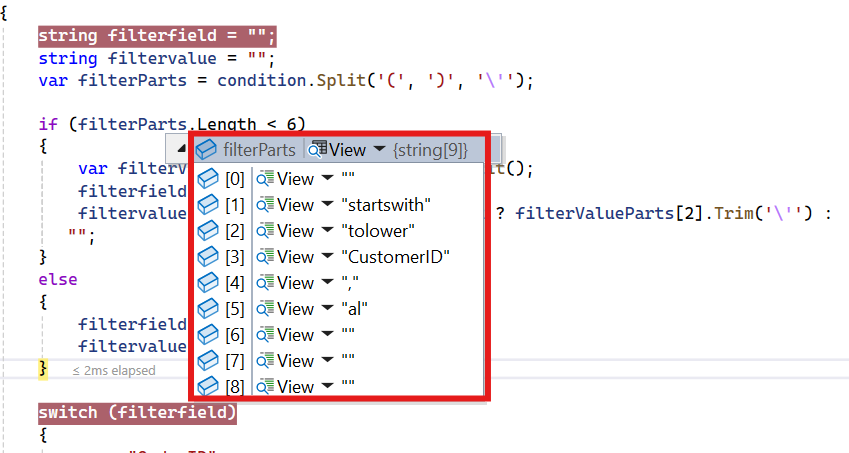
// Split the condition into parts to extract the field and value.
var filterParts = condition.Split('(', ')', '\'');
// Handle cases where the filter condition has fewer parts.
if (filterParts.Length < 6)
{
var filterValueParts = filterParts[1].Split();
filterField = filterValueParts[0];
filterValue = filterValueParts.Length > 2 ? filterValueParts[2].Trim('\'') : "";
}
else
{
filterField = filterParts[3];
filterValue = filterParts[5];
}
// Apply filtering based on the extracted field and value.
switch (filterField)
{
case "OrderID":
data = data.Where(item => item != null && item.OrderID.ToString() == filterValue).ToList();
break;
case "CustomerID":
data = data.Where(item => item != null && item.CustomerID?.ToLower().StartsWith(filterValue.ToLower()) == true).ToList();
break;
case "ShipCity":
data = data.Where(item => item != null && item.ShipCity?.ToLower().StartsWith(filterValue.ToLower()) == true).ToList();
break;
case "ShipCountry":
data = data.Where(item => item != null && item.ShipCountry?.ToLower().StartsWith(filterValue.ToLower()) == true).ToList();
break;
}
}
}
}
// Calculate the total count of records after filtering.
int totalRecordsCount = data.Count();
// Return the filtered data and the total count as a JSON object.
return new { Items = data, count = totalRecordsCount };
}@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Data
@using Syncfusion.Blazor
<SfGrid TValue="OrdersDetails" AllowFiltering="true" Height="348">
<SfDataManager Url="https://localhost:xxxx/api/Grid" Adaptor="Adaptors.WebApiAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field="OrderID" HeaderText="Order ID" Width="120" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="CustomerID" HeaderText="Customer Name" Width="160"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="ShipCity" HeaderText="Ship City" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="ShipCountry" HeaderText="Ship Country" Width="150"></GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</SfGrid>The
$filterparameter can include various conditions, such as substringof, eq (equals), gt (greater than), and more. You can customize the filtering logic based on your specific data structure and requirements.
Handling sorting operation
When sorting is triggered, the $orderby parameter is sent to the server. The $orderby parameter specifies the fields to sort by, along with the sort direction (ascending or descending).
The following example demonstrates how to extract the $orderby parameter and apply sorting logic:
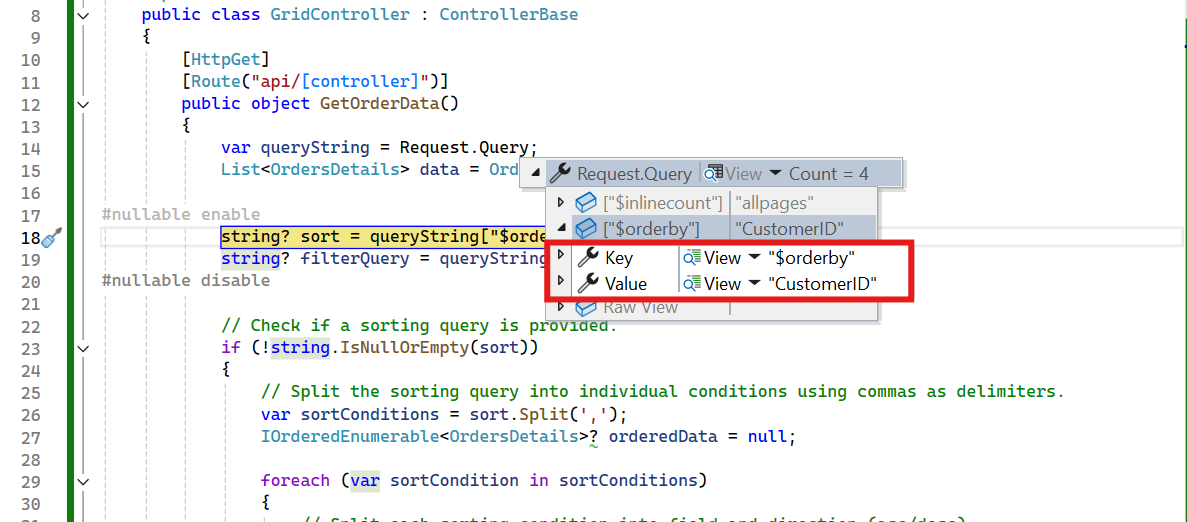
Ascending Sorting
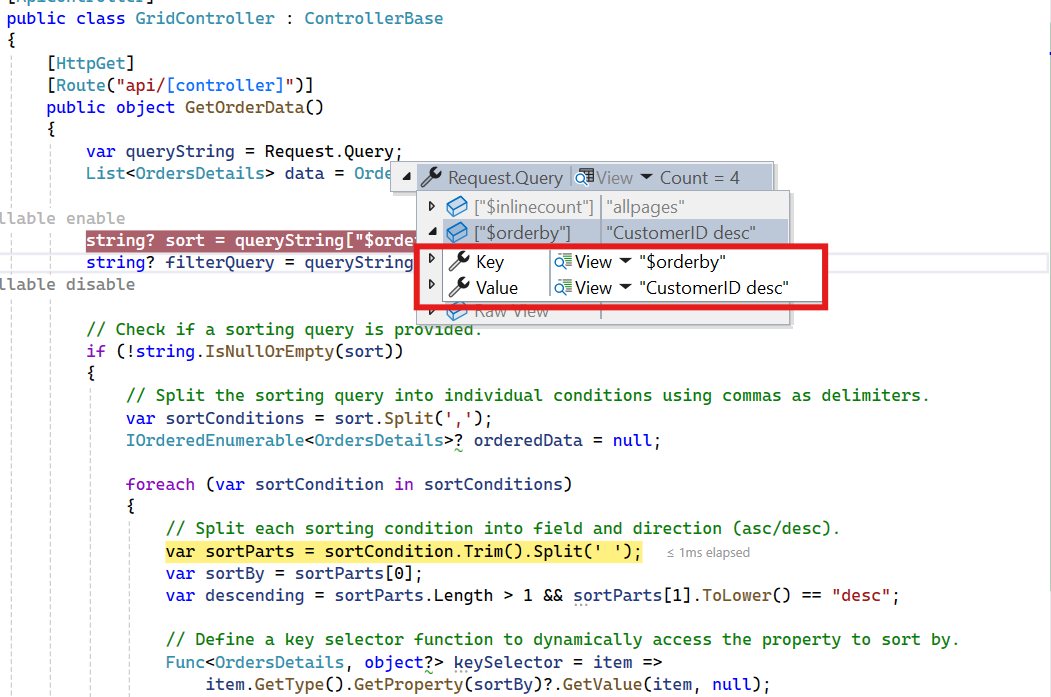
Descending Sorting
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves order data and processes sorting operations based on the provided query parameters.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object containing the sorted list of orders and the total count.</returns>
[HttpGet]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public object GetOrderData()
{
// Retrieve all order records from the data source.
List<OrdersDetails> data = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().ToList();
// Extract the query string from the incoming request.
var queryString = Request.Query;
// Enable nullable reference types for handling sorting queries.
#nullable enable
string? sort = queryString["$orderby"];
#nullable disable
// Check if a sorting query is provided.
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(sort))
{
// Split the sorting query into individual conditions using commas as delimiters.
var sortConditions = sort.Split(',');
IOrderedEnumerable<OrdersDetails>? orderedData = null;
foreach (var sortCondition in sortConditions)
{
// Split each sorting condition into field and direction (asc/desc).
var sortParts = sortCondition.Trim().Split(' ');
var sortBy = sortParts[0];
var descending = sortParts.Length > 1 && sortParts[1].ToLower() == "desc";
// Define a key selector function to dynamically access the property to sort by.
Func<OrdersDetails, object?> keySelector = item =>
item.GetType().GetProperty(sortBy)?.GetValue(item, null);
// Apply sorting based on the field and direction.
orderedData = orderedData == null
? (descending ? data.OrderByDescending(keySelector) : data.OrderBy(keySelector))
: (descending ? orderedData.ThenByDescending(keySelector) : orderedData.ThenBy(keySelector));
}
// Update the data with the sorted result.
if (orderedData != null)
{
data = orderedData.ToList();
}
}
// Calculate the total count of records after sorting.
int totalRecordsCount = data.Count();
// Return the sorted data and the total count as a JSON object.
return new { Items = data, count = totalRecordsCount };
}@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Data
@using Syncfusion.Blazor
<SfGrid TValue="OrdersDetails" AllowSorting="true" Height="348">
<SfDataManager Url="https://localhost:xxxx/api/Grid" Adaptor="Adaptors.WebApiAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field="OrderID" HeaderText="Order ID" Width="120" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="CustomerID" HeaderText="Customer Name" Width="160"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="ShipCity" HeaderText="Ship City" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="ShipCountry" HeaderText="Ship Country" Width="150"></GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</SfGrid>You can parse the
$orderbyparameter to dynamically apply sorting on one or more fields in either ascending or descending order.
Handling paging operation
When paging is applied, the $skip and $top parameters are sent to the server. The $skip parameter specifies the number of records to skip, while the $top parameter specifies how many records to retrieve for the current page.
The following example demonstrates how to apply paging logic:
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves order data and applies paging logic based on the provided query parameters.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Returns a JSON object containing the paged list of orders and the total record count.</returns>
[HttpGet]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public object GetOrderData()
{
// Retrieve all order records from the data source.
List<OrdersDetails> data = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().ToList();
// Extract the query string from the incoming request.
var queryString = Request.Query;
// Calculate the total count of records before applying paging.
int totalRecordsCount = data.Count();
// Extract the number of records to skip from the query string.
int skip = Convert.ToInt32(queryString["$skip"]);
// Extract the number of records to take from the query string.
int take = Convert.ToInt32(queryString["$top"]);
// Apply paging by skipping the specified number of records and taking the required number of records.
return take != 0
? new { Items = data.Skip(skip).Take(take).ToList(), Count = totalRecordsCount }
: new { Items = data, Count = totalRecordsCount };
}@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Data
@using Syncfusion.Blazor
<SfGrid TValue="OrdersDetails" AllowPaging="true" Height="348">
<SfDataManager Url="https://localhost:xxxx/api/Grid" Adaptor="Adaptors.WebApiAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field="OrderID" HeaderText="Order ID" Width="120" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="CustomerID" HeaderText="Customer Name" Width="160"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="ShipCity" HeaderText="Ship City" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="ShipCountry" HeaderText="Ship Country" Width="150"></GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</SfGrid>Always calculate the total record count before applying paging. This ensures that the Grid can display the correct total number of records for pagination.
NOTE
If you want to handle filtering, sorting, and paging operations using Dynamic LINQ Expressions, you can refer to this GitHub repository for an example of how to implement it dynamically.
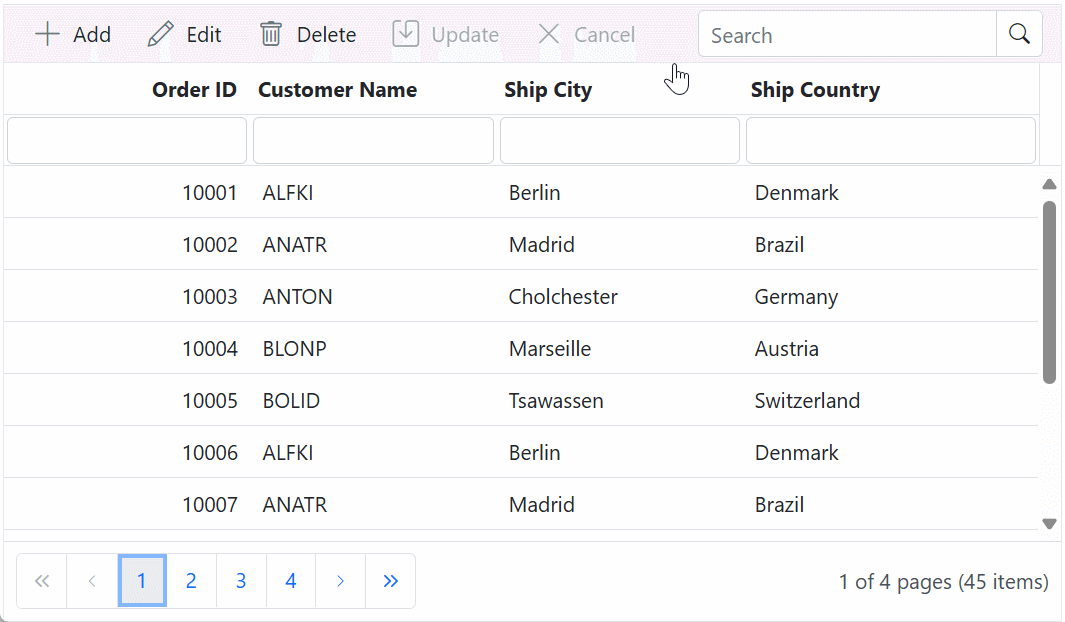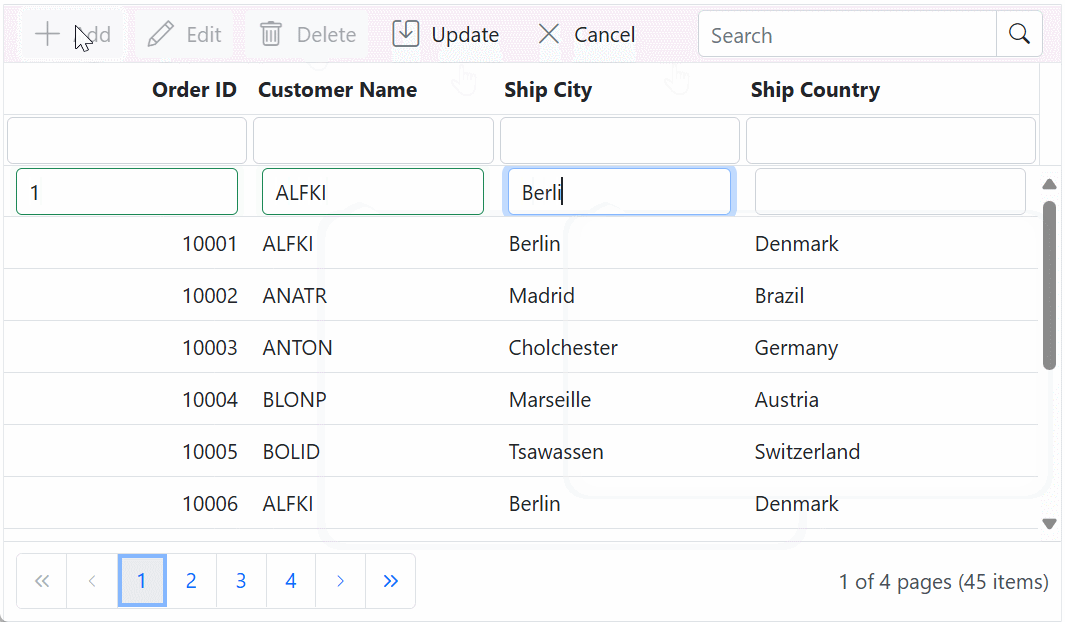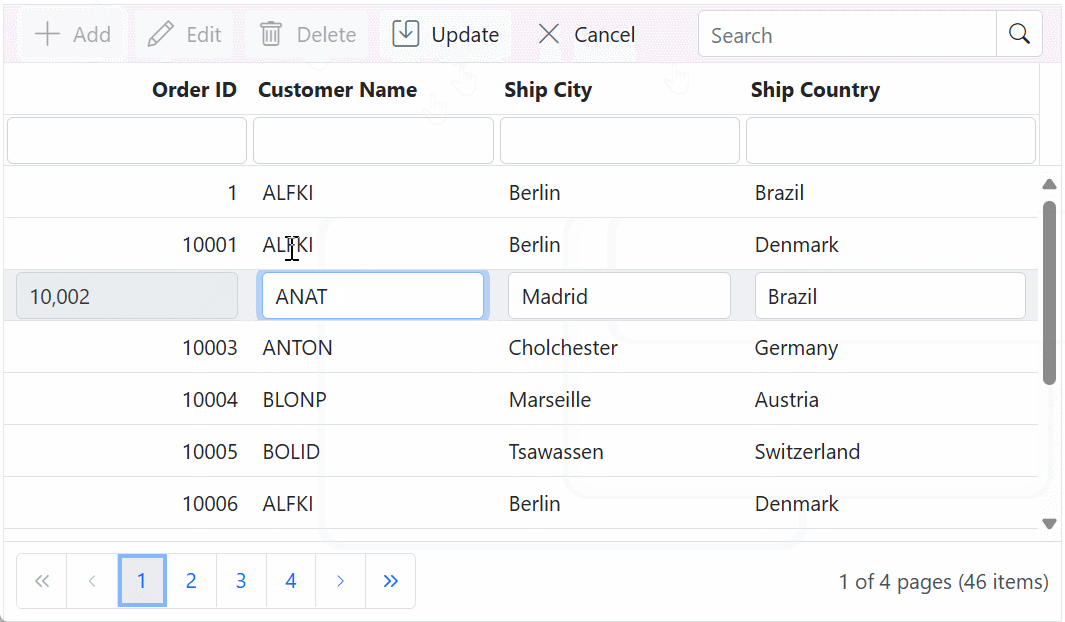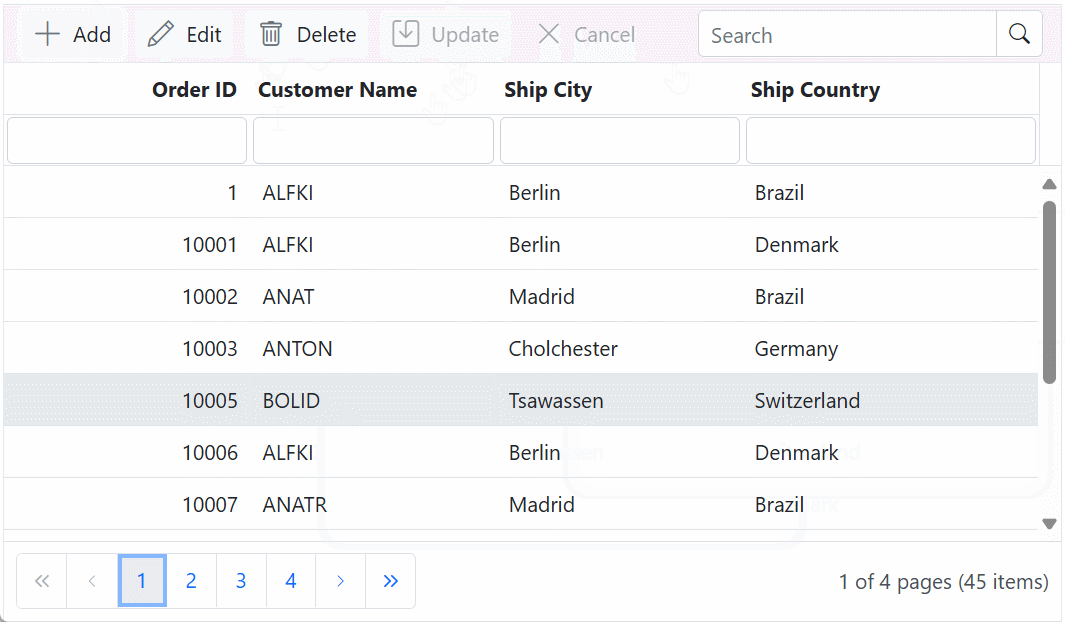
Handling CRUD operations
To manage CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) operations using the WebApiAdaptor in Syncfusion® Blazor DataGrid, follow the provided guide for configuring the Grid for editing and utilize the sample implementation of the GridController in your server application. This controller handles HTTP requests for CRUD operations such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE.
To enable CRUD operations in the Grid, follow the steps below:
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Data
@using Syncfusion.Blazor
<SfGrid TValue="OrdersDetails" Toolbar="@(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel" })" Height="348">
<SfDataManager Url="https://localhost:xxxx/api/Grid" Adaptor="Adaptors.WebApiAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<GridEditSettings AllowEditing="true" AllowDeleting="true" AllowAdding="true" Mode="EditMode.Normal"></GridEditSettings>
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field="OrderID" HeaderText="Order ID" Width="120" IsPrimaryKey="true" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="CustomerID" HeaderText="Customer Name" Width="160"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="ShipCity" HeaderText="Ship City" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="ShipCountry" HeaderText="Ship Country" Width="150"></GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</SfGrid>Normal/Inline editing is the default edit Mode for the Grid. To enable CRUD operations, ensure that the IsPrimaryKey property is set to true for a specific Grid column, ensuring that its value is unique.
Insert operation:
To insert a new record into your Syncfusion® Grid, you can utilize the HttpPost method in your server application. The details of the newly added record are passed to the newRecord parameter. Below is a sample implementation of inserting a record using the GridController:
/// <summary>
/// Inserts a new data item into the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="newRecord">Holds the details of the new record to be inserted.</param>
[HttpPost]
public void Post([FromBody] OrdersDetails newRecord)
{
// Add the new record to the data collection.
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Insert(0, newRecord);
}Update operation:
Updating a record in the Syncfusion® Grid can be achieved by utilizing the HttpPut method in your controller. The details of the updated record are passed to the updatedRecord parameter. Here’s a sample implementation of updating a record:
/// <summary>
/// Update a existing data item from the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="updatedRecord">It contains the updated record detail which is need to be updated.</param>
/// <returns>Returns void.</returns>
public void Put([FromBody] OrdersDetails updatedRecord)
{
var id = updatedRecord.OrderID;
// Find the existing order by id.
var existingOrder = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().FirstOrDefault(o => o.OrderID == id);
if (existingOrder != null)
{
// If the order exists, update its properties.
existingOrder.OrderID = updatedRecord.OrderID;
existingOrder.CustomerID = updatedRecord.CustomerID;
existingOrder.ShipCity = updatedRecord.ShipCity;
existingOrder.ShipCountry = updatedRecord.ShipCountry;
}
}Delete operation:
To delete a record from your Syncfusion® Grid, you can use the HttpDelete method in your controller. The primary key value of the deleted record is passed to the deletedRecord parameter.Below is a sample implementation:
/// <summary>
/// Deletes a specific order record from the data collection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id">The id of the order to delete.</param>
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public void Delete(int id)
{
// Find the existing record that matches the deleted record's "OrderID".
var orderToRemove = OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().FirstOrDefault(order => order.OrderID == id);
// If the order exists, remove it.
if (orderToRemove != null)
{
OrdersDetails.GetAllRecords().Remove(orderToRemove);
}
}
NOTE
ASP.NET Core (Blazor) Web API with batch handling is not yet supported by ASP.NET Core v3+. Therefore, it is currently not feasible to support Batch mode CRUD operations until ASP.NET Core provides support for batch handling. For more details, refer to this GitHub issue.