How can I help you?
Connecting MySQL Server to Blazor Data Grid Using Entity Framework
6 Feb 202624 minutes to read
The Syncfusion® Blazor DataGrid supports binding data from a MySQL Server database using Entity Framework Core (EF Core). This modern approach provides a more maintainable and type-safe alternative to raw SQL queries.
What is Entity Framework Core?
Entity Framework Core (EF Core) is a software tool that simplifies database operations in .NET applications. It serves as a bridge between C# code and databases like MySQL.
Key Benefits of Entity Framework Core
- Automatic SQL Generation: Entity Framework Core generates optimized SQL queries automatically, eliminating the need to write raw SQL code.
- Type Safety: Work with strongly-typed objects instead of raw SQL strings, reducing errors.
- Built-in Security: Automatic parameterization prevents SQL injection attacks.
- Version Control for Databases: Manage database schema changes version-by-version through migrations.
- Familiar Syntax: Use LINQ (Language Integrated Query) syntax, which is more intuitive than raw SQL strings.
What is Pomelo MySQL?
Pomelo MySQL is a software library that helps .NET applications work with a MySQL database using Entity Framework Core. It acts as a bridge between Entity Framework Core and MySQL, allowing applications to read, write, update, and delete data in a MySQL database.
Prerequisites
Ensure the following software and packages are installed before proceeding:
| Software/Package | Version | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Studio 2026 | 18.0 or later | Development IDE with Blazor workload |
| .NET SDK | net8.0 or compatible | Runtime and build tools |
| MySQL Server | 8.0.41 or later | Database server |
| Syncfusion.Blazor.Grid | 32.2.3 | DataGrid and UI components |
| Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes | 32.2.3 | Styling for DataGrid components |
| Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore | 9.0.0 or later | Core framework for database operations |
| Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools | 9.0.0 or later | Tools for managing database migrations |
| Pomelo.EntityFrameworkCore.MySql | 9.0.0 or later | MySQL provider for Entity Framework Core |
Setting Up the MySQL Environment for Entity Framework Core
Step 1: Create the database and Table in MySQL server
First, the MySQL database structure must be created to store transaction records.
Instructions:
- Open MySQL Workbench or any MySQL client.
- Create a new database named
transactiondb. - Define a
transactionstable with the specified schema. - Insert sample data for testing.
Run the following SQL script:
-- Create Database
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS transactiondb;
USE transactiondb;
-- Create Transaction Table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS transactions (
Id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
TransactionId VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
CustomerId INT NOT NULL,
OrderId INT NULL,
InvoiceNumber VARCHAR(50) NULL,
Description VARCHAR(500) NULL,
Amount DECIMAL(15, 2) NOT NULL,
CurrencyCode VARCHAR(10) NULL,
TransactionType VARCHAR(50) NULL,
PaymentGateway VARCHAR(100) NULL,
CreatedOn DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
CompletedOn DATETIME NULL,
Status VARCHAR(50) NULL
);
-- Insert Sample Data (Optional)
INSERT INTO transactions (TransactionId, CustomerId, OrderId, InvoiceNumber, Description, Amount, CurrencyCode, TransactionType, PaymentGateway, CreatedOn, CompletedOn, Status) VALUES
('TXN260113001', 1001, 50001, 'INV-2026-001', 'Samsung S25 Ultra', 153399.00, 'INR', 'SALE', 'Razorpay', '2026-01-13 10:15:30', '2026-01-13 10:16:55', 'SUCCESS'),
('TXN260113002', 1002, 50002, 'INV-2026-002', 'MacBook Pro M4', 224199.00, 'INR', 'SALE', 'Stripe', '2026-01-13 11:20:10', '2026-01-13 11:21:40', 'SUCCESS');After executing this script, the transaction records are stored in the transactions table within the transactiondb database. The database is now ready for integration with the Blazor application.
Step 2: Install Required NuGet Packages
Before installing the necessary NuGet packages, a new Blazor Web Application must be created using the default template.
This template automatically generates essential starter files—such as Program.cs, appsettings.json, the wwwroot folder, and the Components folder.
For this guide, a Blazor application named Grid_MySQL has been created. Once the project is set up, the next step involves installing the required NuGet packages. NuGet packages are software libraries that add functionality to the application. These packages enable Entity Framework Core and MySQL integration.
Method 1: Using Package Manager Console
- Open Visual Studio 2026.
- Navigate to Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Package Manager Console.
- Run the following commands:
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore -Version 9.0.0
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools -Version 9.0.0
Install-Package Pomelo.EntityFrameworkCore.MySql -Version 9.0.0
Install-Package Syncfusion.Blazor.Grid -Version 32.2.3
Install-Package Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes -Version 32.2.3Method 2: Using NuGet Package Manager UI
- Open Visual Studio 2026 → Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Manage NuGet Packages for Solution.
- Search for and install each package individually:
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore (version 9.0.0 or later)
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools (version 9.0.0 or later)
- Pomelo.EntityFrameworkCore.MySql (version 9.0.0 or later)
- Syncfusion.Blazor.Grid (version 32.2.3)
- Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes (version 32.2.3)
All required packages are now installed.
Step 3: Create the Data Model
A data model is a C# class that represents the structure of a database table. This model defines the properties that correspond to the columns in the transactions table.
Instructions:
- Create a new folder named
Datain the Blazor application project. - Inside the
Datafolder, create a new file named TransactionModel.cs. - Define the TransactionModel class with the following code:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace Grid_MySQL.Data
{
/// <summary>
/// Represents a transaction record mapped to the 'transactions' table in the database.
/// This model defines the structure of transaction-related data used throughout the application.
/// </summary>
public class TransactionModel
{
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the unique identifier for the transaction record.
/// </summary>
[Key]
public int Id { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the unique transaction reference generated by the system or payment gateway.
/// </summary>
public string? TransactionId { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the identifier of the customer associated with the transaction.
/// </summary>
public int? CustomerId { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the identifier of the order linked to this transaction.
/// </summary>
public int? OrderId { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the invoice number associated with the transaction.
/// </summary>
public string? InvoiceNumber { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets a description or additional details about the transaction.
/// </summary>
public string? Description { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the monetary amount of the transaction.
/// </summary>
public decimal Amount { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the currency code (e.g., USD, INR, EUR) for the transaction.
/// </summary>
public string? CurrencyCode { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the type of transaction (e.g., Payment, Refund).
/// </summary>
public string? TransactionType { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the payment gateway used to process the transaction.
/// </summary>
public string? PaymentGateway { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the timestamp indicating when the transaction was created.
/// </summary>
public DateTime? CreatedOn { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the timestamp indicating when the transaction was completed.
/// </summary>
public DateTime? CompletedOn { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the current status of the transaction (e.g., Pending, Completed, Failed).
/// </summary>
public string? Status { get; set; }
}
}Explanation:
- The
[Key]attribute marks theIdproperty as the primary key (a unique identifier for each record). - Each property represents a column in the database table.
- The
?symbol indicates that a property is nullable (can be empty).
The data model has been successfully created.
Step 4: Configure the DbContext
A DbContext is a special class that manages the connection between the application and the MySQL database. It handles all database operations such as saving, updating, deleting, and retrieving data.
Instructions:
- Inside the
Datafolder, create a new file named TransactionDbContext.cs. - Define the
TransactionDbContextclass with the following code:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace Grid_MySQL.Data
{
/// <summary>
/// DbContext for Transaction entity
/// Manages database connections and entity configurations
/// </summary>
public class TransactionDbContext : DbContext
{
public TransactionDbContext(DbContextOptions<TransactionDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
/// <summary>
/// DbSet for Transaction entities
/// </summary>
public DbSet<TransactionModel> Transactions => Set<TransactionModel>();
/// <summary>
/// Configures the entity mappings and constraints
/// </summary>
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
// Configure Transaction entity
modelBuilder.Entity<TransactionModel>(entity =>
{
// Primary Key
entity.HasKey(e => e.Id);
// Auto-increment for Primary Key
entity.Property(e => e.Id)
.ValueGeneratedOnAdd();
// Column configurations
entity.Property(e => e.TransactionId)
.HasMaxLength(50)
.IsRequired(true);
entity.Property(e => e.InvoiceNumber)
.HasMaxLength(100)
.IsRequired(false);
entity.Property(e => e.Description)
.HasMaxLength(500)
.IsRequired(false);
entity.Property(e => e.CurrencyCode)
.HasMaxLength(3)
.HasDefaultValue("INR");
entity.Property(e => e.TransactionType)
.HasMaxLength(50)
.IsRequired(false);
entity.Property(e => e.PaymentGateway)
.HasMaxLength(50)
.IsRequired(false);
entity.Property(e => e.Status)
.HasMaxLength(50)
.IsRequired(false);
entity.Property(e => e.Amount)
.HasPrecision(10, 2);
entity.Property(e => e.CustomerId)
.IsRequired(false);
entity.Property(e => e.OrderId)
.IsRequired(false);
entity.Property(e => e.CreatedOn)
.HasColumnType("datetime")
.IsRequired(false);
entity.Property(e => e.CompletedOn)
.HasColumnType("datetime")
.IsRequired(false);
entity.ToTable("transactions");
});
}
}
}Explanation:
- The
DbContextclass inherits from Entity Framework’sDbContextbase class. - The
Transactionsproperty represents thetransactionstable in the database. - The
OnModelCreatingmethod configures how the database columns should behave (maximum length, required/optional, default values, etc.).
The TransactionDbContext class is required because:
- It connects the application to the database.
- It manages all database operations.
- It maps C# models to actual database tables.
- It configures how data should look inside the database.
Without this class, Entity Framework Core will not know where to save data or how to create the transactions table. The DbContext has been successfully configured.
Step 5: Configure the Connection String
A connection string contains the information needed to connect the application to the MySQL database, including the server address, port, database name, and credentials.
Instructions:
- Open the
appsettings.jsonfile in the project root. - Add or update the
ConnectionStringssection with the MySQL connection details:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=localhost;Port=3306;Database=transactiondb;Uid=root;Pwd=mysql@123;SslMode=None;ConvertZeroDateTime=false;"
},
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*"
}Connection String Components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Server | The address of the MySQL server (use localhost for local development) |
| Port | The MySQL port number (default is 3306) |
| Database | The database name (in this case, transactiondb) |
| Uid | The MySQL username (default is root) |
| Pwd | The MySQL password |
| SslMode | SSL encryption mode (set to None for local development) |
| ConvertZeroDateTime | Converts zero datetime values to NULL |
The database connection string has been configured successfully.
Step 6: Create the Repository Class
A repository class is an intermediary layer that handles all database operations. This class uses Entity Framework Core to communicate with the database.
Instructions:
- Inside the
Datafolder, create a new file named TransactionRepository.cs. - Define the TransactionRepository class with the following code:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace Grid_MySQL.Data
{
/// <summary>
/// Repository pattern implementation for Transaction entity using Entity Framework Core
/// Handles all CRUD operations and business logic for transactions
/// </summary>
public class TransactionRepository
{
private readonly TransactionDbContext _context;
public TransactionRepository(TransactionDbContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves all transactions from the database ordered by ID in descending order
/// </summary>
/// <returns>List of all transactions</returns>
public async Task<List<TransactionModel>> GetTransactionsAsync()
{
return await _context.Transactions
.OrderByDescending(t => t.Id)
.ToListAsync();
}
/// <summary>
/// Adds a new transaction to the database
/// </summary>
public async Task AddTransactionAsync(TransactionModel? transaction)
{
// Handle logic to add a new transaction to the database
}
/// <summary>
/// Updates an existing transaction in the database
/// </summary>
public async Task UpdateTransactionAsync(TransactionModel? transaction)
{
// Handle logic to update an existing transaction to the database
}
/// <summary>
/// Deletes a transaction from the database
/// </summary>
public async Task RemoveTransactionAsync(int? transactionId)
{
// Handle logic to delete an existing transaction to the database
}
}
}The repository class has been created.
Step 7: Register Services in Program.cs
The Program.cs file is where application services are registered and configured. This file must be updated to enable Entity Framework Core and the repository pattern.
Instructions:
- Open the
Program.csfile at the project root. - Add the following code after the line
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Grid_MySQL.Data;
using Syncfusion.Blazor;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Get connection string from appsettings.json
var connectionString = builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection");
// Register DbContext with MySQL database
builder.Services.AddDbContext<TransactionDbContext>(options =>
{
options.UseMySql(
connectionString,
ServerVersion.AutoDetect(connectionString)
);
});
// Register the repository for dependency injection
builder.Services.AddScoped<TransactionRepository>();
// Register Syncfusion Blazor services
builder.Services.AddSyncfusionBlazor();
// Add other services as needed
builder.Services.AddRazorComponents()
.AddInteractiveServerComponents();
var app = builder.Build();
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error", createScopeForErrors: true);
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseAntiforgery();
app.MapRazorComponents<App>()
.AddInteractiveServerRenderMode();
app.Run();The service registration has been completed successfully.
Integrating Syncfusion Blazor DataGrid
Step 1: Install and Configure Blazor DataGrid Components
Syncfusion is a library that provides pre-built UI components like DataGrid, which is used to display data in a table format.
Instructions:
- The Syncfusion.Blazor.Grid package was installed in Step 2 of the previous heading.
- Import the required namespaces in the
Components/_Imports.razorfile:
@using Grid_MySQL.Data
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Data
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.DropDowns- Add the Syncfusion stylesheet and scripts in the
Components/App.razorfile. Find the<head>section and add:
<!-- Syncfusion Blazor Stylesheet -->
<link href="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes/tailwind3.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<!-- Syncfusion Blazor Scripts -->
<script src="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Core/scripts/syncfusion-blazor.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>For this project, the tailwind3 theme is used. A different theme can be selected or the existing theme can be customized based on project requirements. Refer to the Syncfusion Blazor Components Appearance documentation to learn more about theming and customization options.
Syncfusion components are now configured and ready to use. For additional guidance, refer to the Grid component’s getting‑started documentation.
Step 2: Update the Blazor DataGrid
The Home.razor component will display the transaction data in a Syncfusion Blazor DataGrid with search, filter, sort, and pagination capabilities.
Instructions:
- Open the file named
Home.razorin theComponents/Pagesfolder. - Add the following code to create a basic DataGrid:
@page "/"
@rendermode InteractiveServer
@inject TransactionRepository TransactionService
<PageTitle>Transaction Management System</PageTitle>
<div class="container-fluid p-4">
<h1 class="mb-4">Transaction Management System</h1>
<p class="mb-3">Manage and view all transaction records from the database.</p>
<!-- Syncfusion Blazor DataGrid Component -->
<SfGrid TValue="TransactionModel" AllowPaging="true" AllowSorting="true" AllowFiltering="true">
<SfDataManager AdaptorInstance="@typeof(CustomAdaptor)" Adaptor="Adaptors.CustomAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<GridColumns>
//columns configuration
</GridColumns>
<GridPageSettings PageSize="10"></GridPageSettings>
</SfGrid>
</div>
@code {
// CustomAdaptor class will be added in the next step
}Component Explanation:
-
@rendermode InteractiveServer: Enables interactive server-side rendering for the component. -
@inject TransactionRepository: Injects the repository to access database methods. -
<SfGrid>: The DataGrid component that displays data in rows and columns. -
<GridColumns>: Defines individual columns in the DataGrid. -
<GridPageSettings>: Configures pagination with 10 records per page.
The Home component has been updated successfully with DataGrid.
Step 3: Implement the CustomAdaptor
The Syncfusion® Blazor DataGrid can bind data from a MySQL Server database using DataManager and set the Adaptor property to CustomAdaptor for scenarios that require full control over data operations.
The CustomAdaptor is a bridge between the DataGrid and the database. It handles all data operations including reading, searching, filtering, sorting, paging, and CRUD operations. Each operation in the CustomAdaptor’s ReadAsync method handles specific grid functionality. The Syncfusion® Blazor DataGrid sends operation details to the API through a DataManagerRequest object. These details can be applied to the data source using methods from the DataOperations class.
Instructions:
- Open the
Components/Pages/Home.razorfile. - Add the following
CustomAdaptorclass code inside the@codeblock:
@code {
private static TransactionRepository? _transactionService;
/// <summary>
/// CustomAdaptor class bridges DataGrid interactions with database operations.
/// This adaptor handles all data retrieval and manipulation for the DataGrid.
/// </summary>
public class CustomAdaptor : DataAdaptor
{
public TransactionRepository? TransactionService
{
get => _transactionService;
set => _transactionService = value;
}
/// <summary>
/// ReadAsync retrieves records from the database and applies data operations.
/// This method executes when the grid initializes and when filtering, searching, sorting, or paging occurs.
/// </summary>
public override async Task<object> ReadAsync(DataManagerRequest dataManagerRequest, string? key = null)
{
try
{
// Fetch all transactions from the database
IEnumerable dataSource = await _transactionService!.GetTransactionsAsync();
// Apply search operation if search criteria exists
if (dataManagerRequest.Search != null && dataManagerRequest.Search.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSearching(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Search);
}
// Apply filter operation if filter criteria exists
if (dataManagerRequest.Where != null && dataManagerRequest.Where.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformFiltering(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Where, dataManagerRequest.Where[0].Operator);
}
// Apply sort operation if sort criteria exists
if (dataManagerRequest.Sorted != null && dataManagerRequest.Sorted.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSorting(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Sorted);
}
// Calculate total record count before paging for accurate pagination
int totalRecordsCount = dataSource.Cast<TransactionModel>().Count();
// Apply paging skip operation
if (dataManagerRequest.Skip != 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSkip(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Skip);
}
// Apply paging take operation to retrieve only the requested page size
if (dataManagerRequest.Take != 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformTake(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Take);
}
// Handling Group operation in CustomAdaptor.
if (dataManagerRequest.Group != null)
{
foreach (var group in dataManagerRequest.Group)
{
dataSource = DataUtil.Group<TransactionModel>(dataSource, group, dataManagerRequest.Aggregates, 0, dataManagerRequest.GroupByFormatter);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method
}
}
// Return the result with total count for pagination metadata
return dataManagerRequest.RequiresCounts
? new DataResult() { Result = dataSource, Count = totalRecordsCount }
: (object)dataSource;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new Exception($"An error occurred while retrieving data: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
}The CustomAdaptor class has been successfully implemented with all data operations.
Common methods in data operations
-
ReadAsync(DataManagerRequest) - Retrieve and process records (search, filter, sort, page, group)
- PerformSearching - Applies search criteria to the collection.
- PerformFiltering - Filters data based on conditions.
- PerformSorting - Sorts data by one or more fields.
- PerformSkip - Skips a defined number of records for paging.
- PerformTake - Retrieves a specified number of records for paging.
- PerformAggregation – Calculates aggregate values such as Sum, Average, Min, and Max.
Step 4: Add Toolbar with CRUD and search options
The toolbar provides buttons for adding, editing, deleting records, and searching the data.
Instructions:
- Open the
Components/Pages/Home.razorfile. - Update the
<SfGrid>component to include the Toolbar property with CRUD and search options:
<SfGrid TValue="TransactionModel"
AllowPaging="true"
AllowSorting="true"
AllowFiltering="true"
Toolbar="@ToolbarItems">
<SfDataManager AdaptorInstance="@typeof(CustomAdaptor)" Adaptor="Adaptors.CustomAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<!-- Grid columns configuration -->
</SfGrid>- Add the toolbar items list in the
@codeblock:
@code {
private List<string> ToolbarItems = new List<string> { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel", "Search"};
// CustomAdaptor class code...
}Toolbar Items Explanation:
| Item | Function |
|---|---|
Add |
Opens a form to add a new transaction record. |
Edit |
Enables editing of the selected record. |
Delete |
Deletes the selected record from the database. |
Update |
Saves changes made to the selected record. |
Cancel |
Cancels the current edit or add operation. |
Search |
Displays a search box to find records. |
The toolbar has been successfully added.
Step 5: Running the Application
Build the Application
- Open the terminal or Package Manager Console.
- Navigate to the project directory.
- Run the following command:
dotnet buildRun the Application
Execute the following command:
dotnet runAccess the Application
- Open a web browser.
- Navigate to
https://localhost:5001(or the port shown in the terminal). - The transaction management application is now running and ready to use.
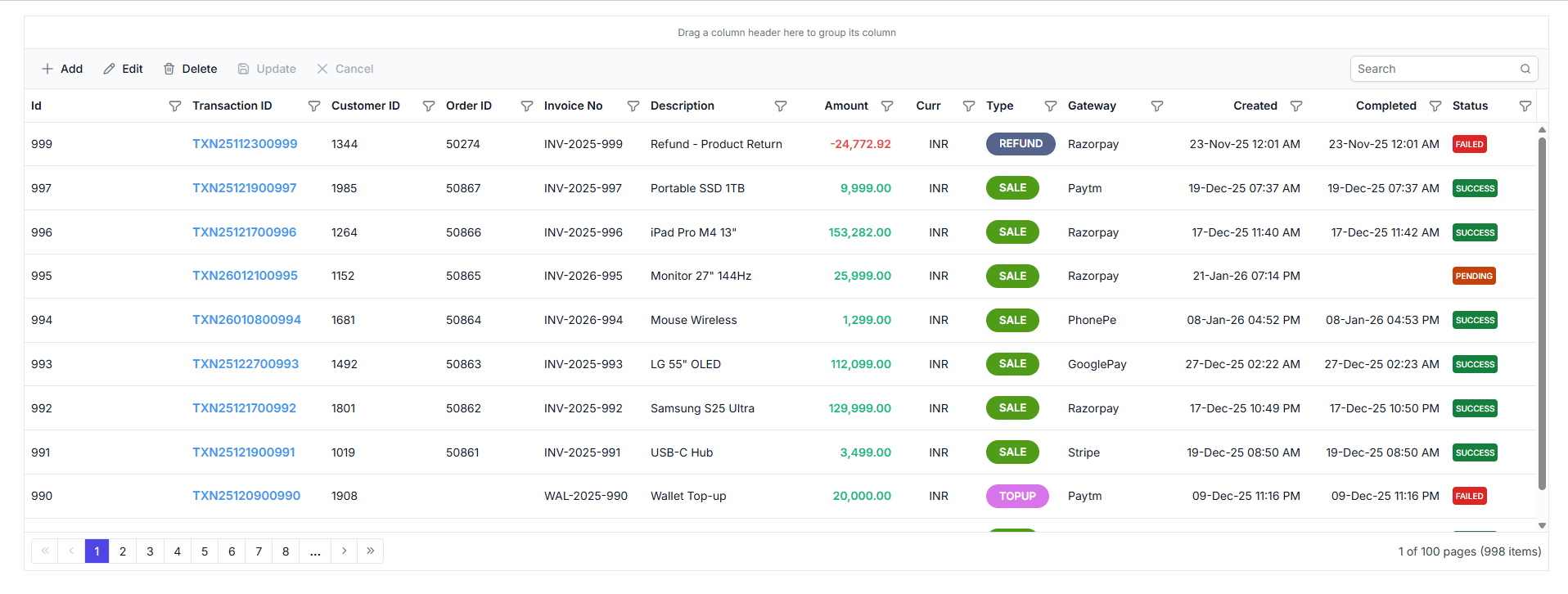
Step 6: Implement Paging Feature
Paging divides large datasets into smaller pages to improve performance and usability.
Instructions:
- The paging feature is already partially enabled in the
<SfGrid>component with AllowPaging=”true”. - The page size is configured with GridPageSettings.
- No additional code changes are required from the previous steps.
<SfGrid TValue="TransactionModel"
AllowPaging="true">
<SfDataManager AdaptorInstance="@typeof(CustomAdaptor)" Adaptor="Adaptors.CustomAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<GridPageSettings PageSize="10"></GridPageSettings>
<!-- Grid columns configuration -->
</SfGrid>- Update the
ReadAsyncmethod in theCustomAdaptorclass to handle paging:
@code {
/// <summary>
/// CustomAdaptor class to handle grid data operations with MySQL using Entity Framework
/// </summary>
public class CustomAdaptor : DataAdaptor
{
public static TransactionRepository? _transactionService { get; set; }
public TransactionRepository? TransactionService
{
get => _transactionService;
set => _transactionService = value;
}
public override async Task<object> ReadAsync(DataManagerRequest dataManagerRequest, string? key = null)
{
IEnumerable dataSource = await _transactionService!.GetTransactionsAsync();
int totalRecordsCount = dataSource.Cast<TransactionModel>().Count();
DataResult dataObject = new DataResult();
// Handling Paging
if (dataManagerRequest.Skip != 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSkip(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Skip);
}
if (dataManagerRequest.Take != 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformTake(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Take);
}
return dataManagerRequest.RequiresCounts
? new DataResult() { Result = dataSource, Count = totalRecordsCount }
: (object)dataSource;
}
}
}Fetches transaction data by calling the GetTransactionsAsync method, which is implemented in the TransactionRepository.cs file.
/// <summary>
/// Retrieves all transactions from the database ordered by ID descending
/// </summary>
/// <returns>List of all transactions</returns>
public async Task<List<TransactionModel>> GetTransactionsAsync()
{
try
{
return await _context.Transactions
.OrderByDescending(t => t.Id)
.ToListAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error retrieving transactions: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}How Paging Works:
- The DataGrid displays 10 records per page (as set in
GridPageSettings). - Navigation buttons allow the user to move between pages.
- When a page is requested, the
ReadAsyncmethod receives skip and take values. - The
DataOperations.PerformSkip()andDataOperations.PerformTake()methods handle pagination. - Only the requested page of records is transmitted from the server.
Paging feature is now active with 10 records per page.
Step 7: Implement Searching feature
Searching allows the user to find records by entering keywords in the search box.
Instructions:
- The search functionality is already enabled in the CustomAdaptor’s
ReadAsyncmethod. - Ensure the toolbar includes the “Search” item.
- No additional code changes are required.
<SfGrid TValue="TransactionModel"
AllowPaging="true
Toolbar="@ToolbarItems">
<SfDataManager AdaptorInstance="@typeof(CustomAdaptor)" Adaptor="Adaptors.CustomAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<GridPageSettings PageSize="10"></GridPageSettings>
<!-- Grid columns configuration -->
</SfGrid>- Update the
ReadAsyncmethod in theCustomAdaptorclass to handle searching:
@code {
private List<string> ToolbarItems = new List<string> { "Search"};
/// <summary>
/// CustomAdaptor class to handle grid data operations with MySQL using Entity Framework
/// </summary>
public class CustomAdaptor : DataAdaptor
{
public static TransactionRepository? _transactionService { get; set; }
public TransactionRepository? TransactionService
{
get => _transactionService;
set => _transactionService = value;
}
public override async Task<object> ReadAsync(DataManagerRequest dataManagerRequest, string? key = null)
{
IEnumerable dataSource = await _transactionService!.GetTransactionsAsync();
// Handling Search
if (dataManagerRequest.Search != null && dataManagerRequest.Search.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSearching(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Search);
}
int totalRecordsCount = dataSource.Cast<TransactionModel>().Count();
// Handling Paging
if (dataManagerRequest.Skip != 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSkip(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Skip);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method
}
if (dataManagerRequest.Take != 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformTake(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Take);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method
}
return dataManagerRequest.RequiresCounts
? new DataResult() { Result = dataSource, Count = totalRecordsCount }
: (object)dataSource;
}
}
}How Searching Works:
- When the user enters text in the search box and presses Enter, the DataGrid sends a search request to the CustomAdaptor.
- The
ReadAsyncmethod receives the search criteria indataManagerRequest.Search. - The
DataOperations.PerformSearching()method filters the data based on the search term. - Results are returned and displayed in the DataGrid.
Searching feature is now active.
Step 8: Implement Filtering feature
Filtering allows the user to restrict data based on column values using a menu interface.
Instructions:
- Open the
Components/Pages/Home.razorfile. - Add the AllowFiltering property and GridFilterSettings to the
<SfGrid>component:
<SfGrid TValue="TransactionModel"
AllowPaging="true"
AllowFiltering="true"
Toolbar="@ToolbarItems">
<SfDataManager AdaptorInstance="@typeof(CustomAdaptor)" Adaptor="Adaptors.CustomAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<GridFilterSettings Type="Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids.FilterType.Menu"></GridFilterSettings>
<!-- Grid columns configuration -->
</SfGrid>- Update the
ReadAsyncmethod in theCustomAdaptorclass to handle filtering:
/// <summary>
/// CustomAdaptor class to handle grid data operations with MySQL using Entity Framework
/// </summary>
public class CustomAdaptor : DataAdaptor
{
public static TransactionRepository? _transactionService { get; set; }
public TransactionRepository? TransactionService
{
get => _transactionService;
set => _transactionService = value;
}
public override async Task<object> ReadAsync(DataManagerRequest dataManagerRequest, string? key = null)
{
IEnumerable dataSource = await _transactionService!.GetTransactionsAsync();
// Handling Search
if (dataManagerRequest.Search != null && dataManagerRequest.Search.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSearching(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Search);
}
// Handling Filtering
if (dataManagerRequest.Where != null && dataManagerRequest.Where.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformFiltering(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Where, dataManagerRequest.Where[0].Operator);
}
int totalRecordsCount = dataSource.Cast<TransactionModel>().Count();
// Handling Paging
if (dataManagerRequest.Skip != 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSkip(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Skip);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method
}
if (dataManagerRequest.Take != 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformTake(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Take);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method
}
return dataManagerRequest.RequiresCounts
? new DataResult() { Result = dataSource, Count = totalRecordsCount }
: (object)dataSource;
}
}How Filtering Works:
- Click on the dropdown arrow in any column header to open the filter menu.
- Select filtering criteria (equals, contains, greater than, less than, etc.).
- Click the “Filter” button to apply the filter.
- The
ReadAsyncmethod receives the filter criteria indataManagerRequest.Where. - Results are filtered accordingly and displayed in the DataGrid.
Filtering feature is now active.
Step 9: Implement Sorting feature
Sorting enables the user to arrange records in ascending or descending order based on column values.
Instructions:
- Open the
Components/Pages/Home.razorfile. - Add the AllowSorting property to the
<SfGrid>component:
<SfGrid TValue="TransactionModel"
AllowPaging="true"
AllowSorting="true"
AllowFiltering="true"
Toolbar="@ToolbarItems">
<SfDataManager AdaptorInstance="@typeof(CustomAdaptor)" Adaptor="Adaptors.CustomAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<GridPageSettings PageSize="10"></GridPageSettings>
<GridFilterSettings Type="Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids.FilterType.Menu"></GridFilterSettings>
<!-- Grid columns configuration -->
</SfGrid>- Update the
ReadAsyncmethod in theCustomAdaptorclass to handle sorting:
/// <summary>
/// CustomAdaptor class to handle grid data operations with MySQL using Entity Framework
/// </summary>
public class CustomAdaptor : DataAdaptor
{
public static TransactionRepository? _transactionService { get; set; }
public TransactionRepository? TransactionService
{
get => _transactionService;
set => _transactionService = value;
}
public override async Task<object> ReadAsync(DataManagerRequest dataManagerRequest, string? key = null)
{
IEnumerable dataSource = await _transactionService!.GetTransactionsAsync();
// Handling Search
if (dataManagerRequest.Search != null && dataManagerRequest.Search.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSearching(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Search);
}
// Handling Filtering
if (dataManagerRequest.Where != null && dataManagerRequest.Where.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformFiltering(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Where, dataManagerRequest.Where[0].Operator);
}
// Handling Sorting
if (dataManagerRequest.Sorted != null && dataManagerRequest.Sorted.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSorting(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Sorted);
}
int totalRecordsCount = dataSource.Cast<TransactionModel>().Count();
// Handling Paging
if (dataManagerRequest.Skip != 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSkip(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Skip);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method
}
if (dataManagerRequest.Take != 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformTake(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Take);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method
}
return dataManagerRequest.RequiresCounts
? new DataResult() { Result = dataSource, Count = totalRecordsCount }
: (object)dataSource;
}
}How Sorting Works:
- Click on the column header to sort in ascending order.
- Click again to sort in descending order.
- The
ReadAsyncmethod receives the sort criteria indataManagerRequest.Sorted. - Records are sorted accordingly and displayed in the DataGrid.
Sorting feature is now active.
Step 10: Implement Grouping feature
Grouping organizes records into hierarchical groups based on column values.
Instructions:
- Open the
Components/Pages/Home.razorfile. - Add the AllowGrouping property to the
<SfGrid>component:
<SfGrid TValue="TransactionModel"
AllowPaging="true"
AllowSorting="true"
AllowFiltering="true"
AllowGrouping="true"
Toolbar="@ToolbarItems">
<SfDataManager AdaptorInstance="@typeof(CustomAdaptor)" Adaptor="Adaptors.CustomAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<GridPageSettings PageSize="10"></GridPageSettings>
<GridFilterSettings Type="Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids.FilterType.Menu"></GridFilterSettings>
<!-- Grid columns -->
</SfGrid>- Update the
ReadAsyncmethod in theCustomAdaptorclass to handle grouping:
/// <summary>
/// CustomAdaptor class to handle grid data operations with MySQL using Entity Framework
/// </summary>
public class CustomAdaptor : DataAdaptor
{
public static TransactionRepository? _transactionService { get; set; }
public TransactionRepository? TransactionService
{
get => _transactionService;
set => _transactionService = value;
}
public override async Task<object> ReadAsync(DataManagerRequest dataManagerRequest, string? key = null)
{
IEnumerable dataSource = await _transactionService!.GetTransactionsAsync();
// Handling Search
if (dataManagerRequest.Search != null && dataManagerRequest.Search.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSearching(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Search);
}
// Handling Filtering
if (dataManagerRequest.Where != null && dataManagerRequest.Where.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformFiltering(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Where, dataManagerRequest.Where[0].Operator);
}
// Handling Sorting
if (dataManagerRequest.Sorted != null && dataManagerRequest.Sorted.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSorting(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Sorted);
}
int totalRecordsCount = dataSource.Cast<TransactionModel>().Count();
// Handling Paging
if (dataManagerRequest.Skip != 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSkip(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Skip);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method
}
if (dataManagerRequest.Take != 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformTake(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Take);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method
}
// Handling Group operation in CustomAdaptor.
if (dataManagerRequest.Group != null)
{
foreach (var group in dataManagerRequest.Group)
{
dataSource = DataUtil.Group<TransactionModel>(dataSource, group, dataManagerRequest.Aggregates, 0, dataManagerRequest.GroupByFormatter);
}
}
return dataManagerRequest.RequiresCounts
? new DataResult() { Result = dataSource, Count = totalRecordsCount }
: (object)dataSource;
}
}How Grouping Works:
- Columns can be grouped by dragging the column header into the group drop area.
- Each group can be expanded or collapsed by clicking on the group header.
- The
ReadAsyncmethod receives the grouping instructions throughdataManagerRequest.Group. - The grouping operation is processed using DataUtil.Group, which organizes the records into hierarchical groups based on the selected column.
- Grouping is performed after search, filter, and sort operations, ensuring the grouped data reflects all applied conditions.
- The processed grouped result is then returned to the Grid and displayed in a structured, hierarchical format.
Grouping feature is now active.
Step 11: Perform CRUD operations
CustomAdaptor methods enable users to create, read, update, and delete records directly from the DataGrid. Each operation calls corresponding data layer methods in TransactionRepository.cs to execute MySQL commands.
Add the Grid EditSettings and Toolbar configuration to enable create, read, update, and delete (CRUD) operations.
<SfGrid TValue="TransactionModel"
AllowPaging="true"
AllowSorting="true"
AllowFiltering="true"
AllowGrouping="true"
Toolbar="@ToolbarItems">
<SfDataManager AdaptorInstance="@typeof(CustomAdaptor)" Adaptor="Adaptors.CustomAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<GridPageSettings PageSize="10"></GridPageSettings>
<GridFilterSettings Type="Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids.FilterType.Menu"></GridFilterSettings>
<GridEditSettings AllowEditing="true" AllowAdding="true" AllowDeleting="true" Mode="EditMode.Normal"></GridEditSettings>
<!-- Grid columns -->
</SfGrid>Add the toolbar items list in the @code block:
@code {
private List<string> ToolbarItems = new List<string> { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel", "Search"};
// CustomAdaptor class code...
}Insert
Record insertion allows new transactions to be added directly through the DataGrid component. The adaptor processes the insertion request, performs any required business‑logic validation, and saves the newly created record to the MySQL Server database.
In Home.razor, implement the InsertAsync method to handle record deletion within the CustomAdaptor class:
public class CustomAdaptor : DataAdaptor
{
public override async Task<object> InsertAsync(DataManager dataManager, object value, string key)
{
await _transactionService!.AddTransactionAsync(value as TransactionModel);
return value;
}
}In Data/TransactionRepository.cs, implement the insert method:
public async Task AddTransactionAsync(TransactionModel? transaction)
{
if (transaction == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(transaction), "Transaction cannot be null");
if (transaction.CreatedOn == null)
transaction.CreatedOn = DateTime.Now;
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(transaction.CurrencyCode))
transaction.CurrencyCode = "INR";
string temporaryTransactionId = GeneratePublicTransactionId(transaction.CreatedOn, 99999);
transaction.TransactionId = temporaryTransactionId;
_context.Transactions.Add(transaction);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
string finalTransactionId = GeneratePublicTransactionId(transaction.CreatedOn, transaction.Id);
transaction.TransactionId = finalTransactionId;
_context.Transactions.Update(transaction);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
private string GeneratePublicTransactionId(DateTime? CreatedOnDate, int primaryKeyId)
{
DateTime dateToUse = CreatedOnDate ?? DateTime.Now;
string datepart = dateToUse.ToString("yyMMdd");
string formattedId = primaryKeyId.ToString("D5");
string transactionId = $"{PublicTransactionIdPrefix}{datepart}{formattedId}";
return transactionId;
}Helper methods explanation:
-
GeneratePublicTransactionId(): A new TransactionId is generated using CreatedOnDate and primaryKeyId.
What happens behind the scenes:
- The form data is collected and validated in the CustomAdaptor’s
InsertAsync()method. - The
TransactionRepository.AddTransactionAsync()method is called. - The new record is added to the
_context.Transactionscollection. -
SaveChangesAsync()persists the record to the MySQL database. - The DataGrid automatically refreshes to display the new record.
Now the new transaction is persisted to the database and reflected in the grid.
Update
Record modification allows transaction details to be updated directly within the DataGrid. The adaptor processes the edited row, validates the updated values, and applies the changes to the MySQL Server database while ensuring data integrity is preserved.
In Home.razor, implement the UpdateAsync method to handle record deletion within the CustomAdaptor class:
public class CustomAdaptor : DataAdaptor
{
public override async Task<object> UpdateAsync(DataManager dataManager, object value, string keyField, string key)
{
await _transactionService!.UpdateTransactionAsync(value as TransactionModel);
return value;
}
}In Data/TransactionRepository.cs, implement the update method:
public async Task UpdateTransactionAsync(TransactionModel? transaction)
{
if (transaction == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(transaction), "Transaction cannot be null");
var existingTransaction = await _context.Transactions.FindAsync(transaction.Id);
if (existingTransaction == null)
throw new KeyNotFoundException($"Transaction with ID {transaction.Id} not found in the database.");
existingTransaction.TransactionId = transaction.TransactionId;
existingTransaction.CustomerId = transaction.CustomerId;
existingTransaction.OrderId = transaction.OrderId;
existingTransaction.InvoiceNumber = transaction.InvoiceNumber;
existingTransaction.Description = transaction.Description;
existingTransaction.Amount = transaction.Amount;
existingTransaction.CurrencyCode = transaction .CurrencyCode;
existingTransaction.TransactionType = transaction.TransactionType;
existingTransaction.PaymentGateway = transaction.PaymentGateway;
existingTransaction.CompletedOn = transaction.CompletedOn;
existingTransaction.Status = transaction.Status;
_context.Transactions.Update(existingTransaction);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
}What happens behind the scenes:
- The modified data is collected from the form.
- The CustomAdaptor’s
UpdateAsync()method is called. - The
TransactionRepository.UpdateTransactionAsync()method is called. - The existing record is retrieved from the database by ID.
- All properties are updated with the new values (except ID and CreatedOn).
-
SaveChangesAsync()persists the changes to the MySQL database. - The DataGrid refreshes to display the updated record.
Now modifications are synchronized to the database and reflected in the grid UI.
Delete
Record deletion allows transactions to be removed directly from the DataGrid. The adaptor captures the delete request, executes the corresponding MySQL DELETE operation, and updates both the database and the grid to reflect the removal.
In Home.razor, implement the RemoveAsync method to handle record deletion within the CustomAdaptor class:
public class CustomAdaptor : DataAdaptor
{
public override async Task<object> RemoveAsync(DataManager dataManager, object value, string keyField, string key)
{
await _transactionService!.RemoveTransactionAsync(value as int?);
return value;
}
}In Data/TransactionRepository.cs, implement the delete method:
public async Task RemoveTransactionAsync(int? key)
{
try
{
if (key == null || key <= 0)
throw new ArgumentException("Transaction ID cannot be null or invalid", nameof(key));
var transaction = await _context.Transactions.FindAsync(key);
if (transaction == null)
throw new KeyNotFoundException($"Transaction with ID {key} not found");
_context.Transactions.Remove(transaction);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
catch (DbUpdateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Database error while deleting transaction: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error deleting transaction: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}What happens behind the scenes:
- The user selects a record and clicks “Delete”.
- A confirmation dialog appears (built into the DataGrid).
- If confirmed, the CustomAdaptor’s
RemoveAsync()method is called. - The
TransactionRepository.RemoveTransactionAsync()method is called. - The record is located in the database by its ID.
- The record is removed from the
_context.Transactionscollection. -
SaveChangesAsync()executes the DELETE statement in MySQL. - The DataGrid refreshes to remove the deleted record from the UI.
Now transactions are removed from the database and the grid UI reflects the changes immediately.
Batch update
Batch operations combine multiple insert, update, and delete actions into a single request, minimizing network overhead and ensuring transactional consistency by applying all changes atomically to the MySQL Server database.
In Home.razor, implement the BatchUpdateAsync method to handle multiple record updates in a single request within the CustomAdaptor class:
public class CustomAdaptor : DataAdaptor
{
public override async Task<object> BatchUpdateAsync(DataManager dataManager, object changed, object added, object deleted, string keyField, string key, int? dropIndex)
{
// Process updated records
if (changed != null)
{
foreach (var record in (IEnumerable<TransactionModel>)changed)
{
await _transactionService!.UpdateTransactionAsync(record);
}
}
// Process newly added records
if (added != null)
{
foreach (var record in (IEnumerable<TransactionModel>)added)
{
await _transactionService!.AddTransactionAsync(record);
}
}
// Process deleted records
if (deleted != null)
{
foreach (var record in (IEnumerable<TransactionModel>)deleted)
{
await _transactionService!.RemoveTransactionAsync(record.Id);
}
}
return key;
}
}This method is triggered when the DataGrid is operating in Batch Edit mode.
What happens behind the scenes:
- The DataGrid collects all added, edited, and deleted records in Batch Edit mode.
- The combined batch request is passed to the CustomAdaptor’s
BatchUpdateAsync()method. - Each modified record is processed using
TransactionRepository.UpdateTransactionAsync(). - Each newly added record is saved using
TransactionRepository.AddTransactionAsync(). - Each deleted record is removed using
TransactionRepository.RemoveTransactionAsync(). - All repository operations persist changes to the MySQL Server database.
- The DataGrid refreshes to display the updated, added, and removed records in a single response.
Now the adaptor supports bulk modifications with atomic database synchronization. All CRUD operations are now fully implemented, enabling comprehensive data management capabilities within the Blazor DataGrid.
Reference links
- InsertAsync(DataManager, object) - Create new records in MySQL Server
- UpdateAsync(DataManager, object, string, string) - Edit existing records in MySQL Server
- RemoveAsync(DataManager, object, string, string) - Delete records from MySQL Server
- BatchUpdateAsync(DataManager, object, object, object, string, string, int?) - Handle bulk operations
Step 12: Complete code
Here is the complete and final Home.razor component with all features integrated:
@page "/"
@rendermode InteractiveServer
@using System.Collections
@inject TransactionRepository TransactionService
<SfGrid TValue="TransactionModel" AllowSorting="true" AllowFiltering="true" AllowGrouping="true" AllowPaging="true"
Height="500px" Width="100%" Toolbar="@(new List<string>() { "Add", "Edit", "Delete", "Update", "Cancel", "Search" })">
<SfDataManager AdaptorInstance="@typeof(CustomAdaptor)" Adaptor="Adaptors.CustomAdaptor"></SfDataManager>
<GridFilterSettings Type="Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids.FilterType.Menu"></GridFilterSettings>
<GridEditSettings AllowEditing="true" AllowAdding="true" AllowDeleting="true" Mode="EditMode.Normal"></GridEditSettings>
<GridPageSettings PageSize="10"></GridPageSettings>
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(TransactionModel.Id) IsPrimaryKey="true" ShowInColumnChooser="false" ShowColumnMenu="false"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(TransactionModel.TransactionId) HeaderText="Transaction ID" Width="170" TextAlign="TextAlign.Left" AllowAdding="false" AllowEditing="false">
<Template>
@{
var data = (TransactionModel)context;
}
<a class="status-text status-ticket-id">
@data.TransactionId
</a>
</Template>
</GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(TransactionModel.CustomerId) HeaderText="Customer ID" Width="140" ValidationRules="@(new ValidationRules { Required = true })" EditType="EditType.NumericEdit" />
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(TransactionModel.OrderId) HeaderText="Order ID" Width="120" ValidationRules="@(new ValidationRules { Required = true })" EditType="EditType.NumericEdit" />
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(TransactionModel.InvoiceNumber) HeaderText="Invoice No" Width="130" EditType="EditType.DefaultEdit" />
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(TransactionModel.Description) HeaderText="Description" Width="180" EditType="EditType.DefaultEdit" />
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(TransactionModel.Amount) HeaderText="Amount" Width="130" ValidationRules="@(new ValidationRules { Required = true })" Format="N2" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right" EditType="EditType.NumericEdit">
<Template>
@{
var amount = (context as TransactionModel)?.Amount ?? 0;
var amountClass = amount < 0 ? "amnt-negative" : "amnt-positive";
}
<span class="@amountClass">@amount.ToString("N2")</span>
</Template>
</GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(TransactionModel.CurrencyCode) HeaderText="Curr" Width="100" TextAlign="TextAlign.Center" EditType="EditType.DefaultEdit" />
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(TransactionModel.TransactionType) HeaderText="Type" Width="100" EditType="EditType.DropDownEdit" EditorSettings="@TypeDropDownParams">
<Template>
@{
var data = (TransactionModel)context;
}
<span class="chip @GetCategoryClass(data)">
@data.TransactionType
</span>
</Template>
</GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(TransactionModel.PaymentGateway) HeaderText="Gateway" Width="130" EditType="EditType.DropDownEdit" EditorSettings="@GatewayDropDownParams" />
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(TransactionModel.CreatedOn) HeaderText="Created" Width="170" Format="dd-MMM-yy hh:mm tt" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right" Type="ColumnType.DateTime" AllowEditing="false" />
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(TransactionModel.CompletedOn) HeaderText="Completed" Width="170" Format="dd-MMM-yy hh:mm tt" TextAlign="TextAlign.Right" Type="ColumnType.DateTime" EditType="EditType.DateTimePickerEdit" />
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(TransactionModel.Status) HeaderText="Status" Width="110" ValidationRules="@(new ValidationRules { Required = true })" EditType="EditType.DropDownEdit" EditorSettings="@StatusDropDownParams">
<Template>
@{
var status = (context as TransactionModel)?.Status;
var badgeClass = status?.ToLower() switch
{
"success" => "e-badge e-badge-success",
"failed" => "e-badge e-badge-danger",
"pending" => "e-badge e-badge-warning",
"processing" => "e-badge e-badge-info",
_ => "e-badge"
};
}
<span class="@badgeClass">@status</span>
</Template>
</GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</SfGrid>
- Set IsPrimaryKey to true for a column that contains unique values.
- If the database includes an auto-generated column, set IsIdentity for that column to disable editing during add or update operations.
- The EditType property can be used to specify the desired editor for each column. 🔗
- The behavior of default editors can be customized using the EditorSettings property of the
GridColumncomponent. 🔗- Type property of the
GridColumncomponent specifies the data type of a grid column.- The Template property that allows rendering custom elements in a column instead of the default field value. 🔗
@code {
private CustomAdaptor? _customAdaptor;
protected override void OnInitialized()
{
// Initialize the CustomAdaptor with the injected TransactionRepository
_customAdaptor = new CustomAdaptor { TransactionService = TransactionService };
}
/// <summary>
/// CustomAdaptor class to handle grid data operations with MySQL using Entity Framework
/// </summary>
public class CustomAdaptor : DataAdaptor
{
public static TransactionRepository? _transactionService { get; set; }
public TransactionRepository? TransactionService
{
get => _transactionService;
set => _transactionService = value;
}
public override async Task<object> ReadAsync(DataManagerRequest dataManagerRequest, string? key = null)
{
IEnumerable dataSource = await _transactionService!.GetTransactionsAsync();
// Handling Search
if (dataManagerRequest.Search != null && dataManagerRequest.Search.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSearching(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Search);
}
// Handling Filtering
if (dataManagerRequest.Where != null && dataManagerRequest.Where.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformFiltering(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Where, dataManagerRequest.Where[0].Operator);
}
// Handling Sorting
if (dataManagerRequest.Sorted != null && dataManagerRequest.Sorted.Count > 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSorting(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Sorted);
}
int totalRecordsCount = dataSource.Cast<TransactionModel>().Count();
// Handling Paging
if (dataManagerRequest.Skip != 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformSkip(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Skip);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method
}
if (dataManagerRequest.Take != 0)
{
dataSource = DataOperations.PerformTake(dataSource, dataManagerRequest.Take);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method
}
// Handling Group operation in CustomAdaptor.
if (dataManagerRequest.Group != null)
{
foreach (var group in dataManagerRequest.Group)
{
dataSource = DataUtil.Group<TransactionModel>(dataSource, group, dataManagerRequest.Aggregates, 0, dataManagerRequest.GroupByFormatter);
//Add custom logic here if needed and remove above method
}
}
return dataManagerRequest.RequiresCounts
? new DataResult() { Result = dataSource, Count = totalRecordsCount }
: (object)dataSource;
}
public override async Task<object> InsertAsync(DataManager dataManager, object value, string? key)
{
await _transactionService!.AddTransactionAsync(value as TransactionModel);
return value;
}
public override async Task<object> UpdateAsync(DataManager dataManager, object value, string? keyField, string key)
{
await _transactionService!.UpdateTransactionAsync(value as TransactionModel);
return value;
}
public override async Task<object> RemoveAsync(DataManager dataManager, object value, string? keyField, string key)
{
await _transactionService!.RemoveTransactionAsync(value as int?);
return value;
}
public override async Task<object> BatchUpdateAsync(DataManager dataManager, object changedRecords, object addedRecords, object deletedRecords, string? keyField, string key, int? dropIndex)
{
if (changedRecords != null)
{
foreach (var record in (IEnumerable<TransactionModel>)changedRecords)
{
await _transactionService!.UpdateTransactionAsync(record as TransactionModel);
}
}
if (addedRecords != null)
{
foreach (var record in (IEnumerable<TransactionModel>)addedRecords)
{
await _transactionService!.AddTransactionAsync(record as TransactionModel);
}
}
if (deletedRecords != null)
{
foreach (var record in (IEnumerable<TransactionModel>)deletedRecords)
{
await _transactionService!.RemoveTransactionAsync((record as TransactionModel).Id);
}
}
return key;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Provides a list of payment gateway options used as a data source for the Gateway dropdown editor in the grid.
/// </summary>
private static List<TransactionModel> CustomGateway = new List<TransactionModel> {
new TransactionModel() { PaymentGateway = "Razorpay" },
new TransactionModel() { PaymentGateway= "GooglePay" },
new TransactionModel() { PaymentGateway= "Stripe" },
new TransactionModel() { PaymentGateway= "PhonePe" },
new TransactionModel() { PaymentGateway= "Paytm" },
};
/// <summary>
/// Provides a list of transaction types used as a data source for the Type dropdown editor in the grid.
/// </summary>
private static List<TransactionModel> CustomType = new List<TransactionModel> {
new TransactionModel() { TransactionType = "SALE" },
new TransactionModel() { TransactionType = "REFUND" },
new TransactionModel() { TransactionType = "TOPUP" },
};
/// <summary>
/// Provides a list of transaction statuses used as a data source for the Status dropdown editor in the grid.
/// </summary>
private static List<TransactionModel> CustomStatus = new List<TransactionModel> {
new TransactionModel() { Status = "SUCCESS" },
new TransactionModel() { Status = "PROCESSING" },
new TransactionModel() { Status = "PENDING" },
new TransactionModel() { Status = "FAILED" },
};
/// <summary>
/// Dropdown editor settings configured with payment gateway options for the PaymentGateway column in grid edit mode.
/// </summary>
private IEditorSettings GatewayDropDownParams = new DropDownEditCellParams
{
Params = new DropDownListModel<object, object>() { DataSource = CustomGateway, Query = new Syncfusion.Blazor.Data.Query() },
};
/// <summary>
/// Dropdown editor settings configured with transaction type options for the TransactionType column in grid edit mode.
/// </summary>
private IEditorSettings TypeDropDownParams = new DropDownEditCellParams
{
Params = new DropDownListModel<object, object>() { DataSource = CustomType, Query = new Syncfusion.Blazor.Data.Query() },
};
/// <summary>
/// Dropdown editor settings configured with transaction status options for the Status column in grid edit mode.
/// </summary>
private IEditorSettings StatusDropDownParams = new DropDownEditCellParams
{
Params = new DropDownListModel<object, object>() { DataSource = CustomStatus, Query = new Syncfusion.Blazor.Data.Query() },
};
/// <summary>
/// Returns a CSS class name based on the transaction type to apply visual styling in the grid template.
/// </summary>
private string GetCategoryClass(TransactionModel data)
{
return data.TransactionType?.ToLower() switch
{
"sale" => "category-sale",
"topup" => "category-topup",
"refund" => "category-refund",
_ => ""
};
}
}Complete Sample Repository
A complete, working sample implementation is available in the GitHub repository.
Summary
This guide demonstrates how to:
- Create a MySQL database with transaction records. 🔗
- Install necessary NuGet packages for Entity Framework Core and Syncfusion. 🔗
- Create data models and DbContext for database communication. 🔗
- Configure connection strings and register services. 🔗
- Implement the repository pattern for data access. 🔗
- Create a Blazor component with a DataGrid that supports searching, filtering, sorting, paging, and CRUD operations. 🔗
- Handle bulk operations and batch updates. 🔗
The application now provides a complete solution for managing transaction data with a modern, user-friendly interface.