How can I help you?
Getting Started with Blazor Diagram Component in Web App
29 Jan 202624 minutes to read
This section briefly explains how to include the Blazor Diagram component in your Blazor Web App using Visual Studio, Visual Studio Code, and the .NET CLI.
Ready to streamline your Syncfusion® Blazor development?
Discover the full potential of Syncfusion® Blazor components with Syncfusion® AI Coding Assistants. Effortlessly integrate, configure, and enhance your projects with intelligent, context-aware code suggestions, streamlined setups, and real-time insights—all seamlessly integrated into your preferred AI-powered IDEs like VS Code, Cursor, Syncfusion® CodeStudio and more. Explore Syncfusion® AI Coding Assistants
Prerequisites
Step 1: How to Create a New Blazor Web App
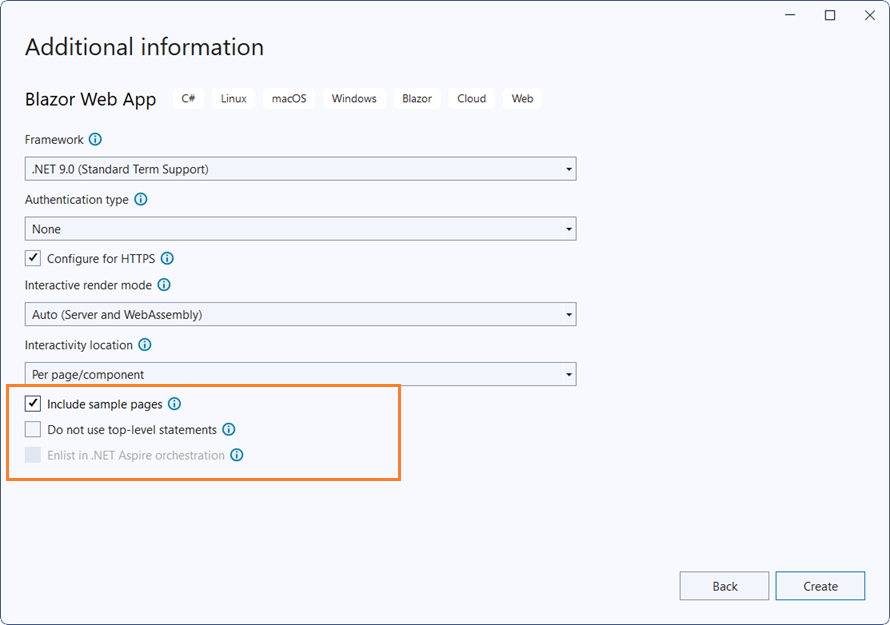
Create a Blazor Web App using Visual Studio 2022 via Microsoft Templates or the Syncfusion® Blazor Extension. For detailed instructions, refer to this Blazor Web App Getting Started documentation.
Configure the appropriate Interactive render mode and Interactivity location while creating a Blazor Web App.
Step 2: How to Install Syncfusion® Blazor Diagram and Themes NuGet Packages in the Blazor Web App
To add the Blazor Diagram component in the app, open the NuGet package manager in Visual Studio (Tools → NuGet Package Manager → Manage NuGet Packages for Solution), then search and install Syncfusion.Blazor.Diagram and Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes.
If using the WebAssembly or Auto render modes in the Blazor Web App, install Syncfusion® Blazor component NuGet packages in the client project.
Alternatively, run the following commands in the Package Manager Console to achieve the same.
Install-Package Syncfusion.Blazor.Diagram -Version 32.2.3
Install-Package Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes -Version 32.2.3NOTE
Syncfusion® Blazor components are available on nuget.org. Refer to the NuGet packages topic for the available NuGet packages list with component details.
Step 3: Add Import Namespaces
Open the ~/_Imports.razor file in the client project and import the Syncfusion.Blazor and Syncfusion.Blazor.Diagram namespaces.
@using Syncfusion.Blazor
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.DiagramStep 4: How to Register Syncfusion® Blazor Service
Register the Syncfusion® Blazor service in the ~/Program.cs file of your Blazor Web App.
If the Interactive Render Mode is set to WebAssembly or Auto, register the Syncfusion® Blazor service in the ~/Program.cs files of the main server project and associated .Client project.
...
...
using Syncfusion.Blazor;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorComponents()
.AddInteractiveServerComponents()
.AddInteractiveWebAssemblyComponents();
builder.Services.AddSyncfusionBlazor();
var app = builder.Build();
.......
using Syncfusion.Blazor;
var builder = WebAssemblyHostBuilder.CreateDefault(args);
builder.Services.AddSyncfusionBlazor();
await builder.Build().RunAsync();Step 5: How to Add Stylesheet and Script Resources
The theme stylesheet and script can be accessed from NuGet through Static Web Assets. Include the stylesheet reference to the <head> section and the script reference at the end of the <body> in the ~/Components/App.razor file as shown below:
<head>
....
<link href="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
....
<body>
....
<script src="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Core/scripts/syncfusion-blazor.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</body>
NOTE
Check out the Blazor Themes topic to discover various methods (Static Web Assets, CDN, and CRG) for referencing themes in your Blazor application. Also, check out the Adding Script Reference topic to learn different approaches for adding script references in your Blazor application.
Step 6: How to Add Syncfusion® Blazor Diagram Component
Add the Syncfusion® Blazor Diagram component to a Razor page located under the Pages folder (e.g., Pages/Home.razor) in either the Server or Client project. When creating a Blazor Web App with the interactive mode set to WebAssembly, the Syncfusion Blazor Diagram component should be rendered within the client application. If the interactivity location is Per page/component in the web app, define a render mode at the top of the component as follows:
| Interactivity location | RenderMode | Code |
|---|---|---|
| Per page/component | Auto | @rendermode InteractiveAuto |
| WebAssembly | @rendermode InteractiveWebAssembly | |
| None | — |
NOTE
If the Interactivity Location is set to
Globaland the Render Mode is set toAutoorWebAssembly, the render mode is configured in theApp.razorfile by default.
@* desired render mode define here *@
@rendermode InteractiveAuto<SfDiagramComponent Width="100%" Height="600px"/>- Press Ctrl+F5 (Windows) or ⌘+F5 (macOS) to launch the application. This will render the Syncfusion® Blazor Diagram component in the default web browser.
Prerequisites
Step 1: How to Create a New Blazor Web App in Visual Studio Code
- Open Visual Studio Code.
- Press Ctrl + ` to open the integrated terminal.
- Execute the following command to create a Blazor Web App with Auto Interactive render mode:
dotnet new blazor -o BlazorWebApp -int Auto
cd BlazorWebApp
cd BlazorWebApp.ClientNOTE
Configure the appropriate interactive render mode and interactivity location when setting up a Blazor Web App. For detailed information, refer to the interactive render mode documentation.
Alternatively, create Blazor Web App using Visual Studio Code via Microsoft Templates or the Syncfusion® Blazor Extension. For detailed instructions, refer to this Blazor Web App Getting Started documentation.
Step 2: How to Install Syncfusion® Blazor Diagram and Themes NuGet Packages in the App
If using the WebAssembly or Auto render modes in the Blazor Web App, install Syncfusion® Blazor component NuGet packages in the client project.
- Press Ctrl+` to open the integrated terminal in Visual Studio Code.
- Ensure the current directory is the project root directory where your
.csprojfile is located. - Run the following command to install the Syncfusion.Blazor.Diagram and Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes NuGet package, and ensure all dependencies are installed.
dotnet add package Syncfusion.Blazor.Diagram -v 32.2.3
dotnet add package Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes -v 32.2.3
dotnet restoreNOTE
Syncfusion® Blazor components are available on nuget.org. Refer to the NuGet packages topic for available NuGet packages list with component details.
Step 3: Add Import Namespaces
Open the ~/_Imports.razor file in the client project and import the Syncfusion.Blazor and Syncfusion.Blazor.Diagram namespaces.
@using Syncfusion.Blazor
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.DiagramStep 4: How to Register Syncfusion® Blazor Service
Register the Syncfusion® Blazor service in the ~/Program.cs file of your Blazor Web App.
If the Interactive Render Mode is set to WebAssembly or Auto, register the Syncfusion® Blazor service in the ~/Program.cs files of the main server project and associated .Client project.
...
...
using Syncfusion.Blazor;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorComponents()
.AddInteractiveServerComponents()
.AddInteractiveWebAssemblyComponents();
builder.Services.AddSyncfusionBlazor();
var app = builder.Build();
.......
using Syncfusion.Blazor;
var builder = WebAssemblyHostBuilder.CreateDefault(args);
builder.Services.AddSyncfusionBlazor();
await builder.Build().RunAsync();Step 5: How to Add Stylesheet and Script Resources
Theme stylesheet and script can be accessed from NuGet through Static Web Assets. Include the stylesheet reference in the <head> section and the script reference at the end of the <body> in the ~/Components/App.razor file as shown below:
<head>
....
<link href="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
....
<body>
....
<script src="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Core/scripts/syncfusion-blazor.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</body>
NOTE
Check out the Blazor Themes topic to discover various methods (Static Web Assets, CDN, and CRG) for referencing themes in your Blazor application. Also, check out the Adding Script Reference topic to learn different approaches for adding script references in your Blazor application.
Step 6: How to Add Syncfusion® Blazor Diagram Component
Add the Syncfusion® Blazor Diagram component to a Razor page located under the Pages folder (e.g., Pages/Home.razor) in either the Server or Client project. When creating a Blazor Web App with the interactive mode set to WebAssembly, the Syncfusion Blazor Diagram component should be rendered within the client application. If the interactivity location is Per page/component in the web app, define a render mode at the top of the component as follows:
| Interactivity location | RenderMode | Code |
|---|---|---|
| Per page/component | Auto | @rendermode InteractiveAuto |
| WebAssembly | @rendermode InteractiveWebAssembly | |
| None | — |
NOTE
If the Interactivity Location is set to
Globaland the Render Mode is set toAutoorWebAssembly, the render mode is configured in theApp.razorfile by default.
@* desired render mode define here *@
@rendermode InteractiveAuto<SfDiagramComponent Width="100%" Height="600px"/>How to run the project:
- Press Ctrl+` to open the integrated terminal in Visual Studio Code.
- Ensure the terminal’s current directory is the server project folder.
- Run the application with:
dotnet run - The running server prints the URL (e.g., https://localhost:5001); open that in a browser to view the rendered SfDiagramComponent.
Prerequisites
Install the latest version of .NET SDK. If you previously installed the SDK, determine the installed version by executing the following command in a command prompt (Windows) or terminal (macOS) or command shell (Linux).
dotnet --versionStep 1: Create a Blazor Web App using .NET CLI
Run the following command to create a new Blazor Web App in a command prompt (Windows) or terminal (macOS) or command shell (Linux). For detailed instructions, refer to this Blazor Web App Getting Started documentation.
Configure the appropriate interactive render mode and interactivity location when setting up the Blazor Web Application. For more information, refer to the interactive render mode documentation.
For example, to create a Blazor Web App with the Auto interactive render mode, use the following commands:
dotnet new blazor -o BlazorApp -int Auto
cd BlazorApp
cd BlazorApp.ClientThis command creates a new Blazor Web App and places it in a new directory called BlazorApp inside your current location. See the Create a Blazor App and dotnet new CLI command topics for more details.
Step 2: Install Syncfusion® Blazor Diagram and Themes NuGet in the App
Here’s an example of how to add Blazor Diagram component in the application using the following command in the command prompt (Windows) or terminal (Linux and macOS) to install a Syncfusion.Blazor.Diagram and Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes NuGet package. See Install and manage packages using the dotnet CLI topics for more details.
If using the WebAssembly or Auto render modes in the Blazor Web App, install Syncfusion® Blazor component NuGet packages in the client project.
dotnet add package Syncfusion.Blazor.Diagram --version 32.2.3
dotnet add package Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes --version 32.2.3
dotnet restoreNOTE
Syncfusion® Blazor components are available on nuget.org. Refer to the NuGet packages topic for the available NuGet packages list with component details.
Step 3: Add Import Namespaces
Open the ~/_Imports.razor file from the client project and import the Syncfusion.Blazor and Syncfusion.Blazor.Diagram namespaces.
@using Syncfusion.Blazor
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.DiagramStep 4: How to Register Syncfusion® Blazor Service
Register the Syncfusion® Blazor service in the ~/Program.cs file of your Blazor Web App.
If the Interactive Render Mode is set to WebAssembly or Auto, register the Syncfusion® Blazor service in the ~/Program.cs files of the main server project and associated .Client project.
...
...
using Syncfusion.Blazor;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorComponents()
.AddInteractiveServerComponents()
.AddInteractiveWebAssemblyComponents();
builder.Services.AddSyncfusionBlazor();
var app = builder.Build();
.......
using Syncfusion.Blazor;
var builder = WebAssemblyHostBuilder.CreateDefault(args);
builder.Services.AddSyncfusionBlazor();
await builder.Build().RunAsync();Step 5: How to Add Stylesheet and Script Resources
Theme stylesheet and script can be accessed from NuGet through Static Web Assets. Include the stylesheet reference in the <head> section and the script reference at the end of the <body> in the ~/Components/App.razor file as shown below:
<head>
....
<link href="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
....
<body>
....
<script src="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Core/scripts/syncfusion-blazor.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</body>
NOTE
Check out the Blazor Themes topic to discover various methods (Static Web Assets, CDN, and CRG) for referencing themes in your Blazor application. Also, check out the Adding Script Reference topic to learn different approaches for adding script references in your Blazor application.
Step 6: How to Add Syncfusion® Blazor Diagram Component
Add the Syncfusion® Blazor Diagram component to a Razor page located under the Pages folder (e.g., Pages/Home.razor) in either the Server or Client project. When creating a Blazor Web App with the interactive mode set to WebAssembly, the Syncfusion Blazor Diagram component should be rendered within the client application. If the interactivity location is Per page/component in the web app, define a render mode at the top of the component as follows:
| Interactivity location | RenderMode | Code |
|---|---|---|
| Per page/component | Auto | @rendermode InteractiveAuto |
| WebAssembly | @rendermode InteractiveWebAssembly | |
| None | — |
NOTE
If the Interactivity Location is set to
Globaland the Render Mode is set toAutoorWebAssembly, the render mode is configured in theApp.razorfile by default.
@* desired render mode define here *@
@rendermode InteractiveAuto<SfDiagramComponent Width="100%" Height="600px"/>Run the app from the command line (Windows) by opening a terminal at the server/project folder (the folder containing the project .csproj that hosts the app) and executing dotnet run command.
Ways to open a terminal at the server project folder:
- File Explorer → navigate to the server project folder → click the address bar, type cmd or PowerShell, press Enter (opens Command Prompt or PowerShell at that path).
- File Explorer → Shift + Right-click in the folder whitespace → choose “Open PowerShell window here” or “Open in Terminal”.
- Run the application with:
dotnet run - The running server prints the URL (e.g., https://localhost:5001); open that in a browser to view the rendered SfDiagramComponent.
Basic Blazor Diagram Elements
- Node: Visualize any graphical object using nodes, which can be arranged and manipulated at the same time on a Blazor diagram page.
- Connector: Represents the relationship between two nodes. Three types of connectors provided as follows:
1) Orthogonal
2) Bezier
3) Straight - Port: Acts as the connection points of node or connector and allow creating connections only at specific points.
- Annotation: Additional information can be shown by adding text or labels on nodes and connectors.
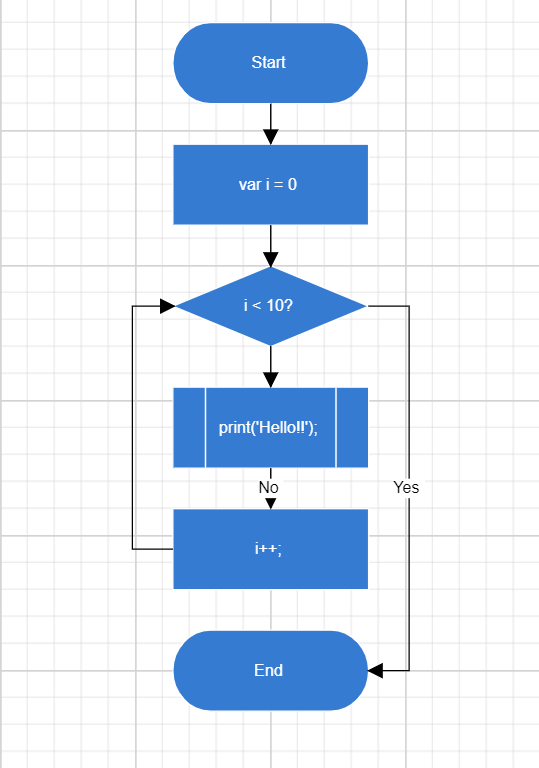
How to Create Blazor Flowchart Diagram
Create and add a Node with specific position, size, label, and shape. Connect two or more nodes using a Connector.
<SfDiagramComponent @ref="@diagram" Connectors="@connectors" Height="700px" Nodes="@nodes" />
@code
{
SfDiagramComponent diagram;
int connectorCount = 0;
//Defines Diagram's nodes collection.
DiagramObjectCollection<Node> nodes = new DiagramObjectCollection<Node>();
//Defines Diagram's connectors collection.
DiagramObjectCollection<Connector> connectors = new DiagramObjectCollection<Connector>();
protected override void OnInitialized()
{
InitDiagramModel();
}
private void InitDiagramModel()
{
CreateNode("Start", 300, 50, NodeFlowShapes.Terminator, "Start");
CreateNode("Init", 300, 140, NodeFlowShapes.Process, "var i = 0");
CreateNode("Condition", 300, 230, NodeFlowShapes.Decision, "i < 10?");
CreateNode("Print", 300, 320, NodeFlowShapes.PreDefinedProcess, "print(\'Hello!!\');");
CreateNode("Increment", 300, 410, NodeFlowShapes.Process, "i++;");
CreateNode("End", 300, 500, NodeFlowShapes.Terminator, "End");
// Creates orthogonal connector.
OrthogonalSegment segment1 = new OrthogonalSegment()
{
Type = ConnectorSegmentType.Orthogonal,
Direction = Direction.Right,
Length = 30,
};
OrthogonalSegment segment2 = new OrthogonalSegment()
{
Type = ConnectorSegmentType.Orthogonal,
Length = 300,
Direction = Direction.Bottom,
};
OrthogonalSegment segment3 = new OrthogonalSegment()
{
Type = ConnectorSegmentType.Orthogonal,
Length = 30,
Direction = Direction.Left,
};
OrthogonalSegment segment4 = new OrthogonalSegment()
{
Type = ConnectorSegmentType.Orthogonal,
Length = 200,
Direction = Direction.Top,
};
CreateConnector("Start", "Init");
CreateConnector("Init", "Condition");
CreateConnector("Condition", "Print");
CreateConnector("Condition", "End", "Yes", segment1, segment2);
CreateConnector("Print", "Increment", "No");
CreateConnector("Increment", "Condition", null, segment3, segment4);
}
// Method to create connector.
private void CreateConnector(string sourceId, string targetId, string label = default(string), OrthogonalSegment segment1 = null, OrthogonalSegment segment2 = null)
{
Connector diagramConnector = new Connector()
{
// Represents the unique id of the connector.
ID = string.Format("connector{0}", ++connectorCount),
SourceID = sourceId,
TargetID = targetId,
};
if (label != default(string))
{
// Represents the annotation of the connector.
PathAnnotation annotation = new PathAnnotation()
{
Content = label,
Style = new TextStyle() { Fill = "white" }
};
diagramConnector.Annotations = new DiagramObjectCollection<PathAnnotation>() { annotation };
}
if (segment1 != null)
{
// Represents the segment type of the connector.
diagramConnector.Type = ConnectorSegmentType.Orthogonal;
diagramConnector.Segments = new DiagramObjectCollection<ConnectorSegment> { segment1, segment2 };
}
connectors.Add(diagramConnector);
}
// Method to create node.
private void CreateNode(string id, double x, double y, NodeFlowShapes shape, string label)
{
Node diagramNode = new Node()
{
//Represents the unique id of the node.
ID = id,
// Defines the position of the node.
OffsetX = x,
OffsetY = y,
// Defines the size of the node.
Width = 145,
Height = 60,
// Defines the style of the node.
Style = new ShapeStyle { Fill = "#357BD2", StrokeColor = "White" },
// Defines the shape of the node.
Shape = new FlowShape() { Type = NodeShapes.Flow, Shape = shape },
// Defines the annotation collection of the node.
Annotations = new DiagramObjectCollection<ShapeAnnotation>
{
new ShapeAnnotation
{
Content = label,
Style = new TextStyle()
{
Color="White",
Fill = "transparent"
}
}
}
};
nodes.Add(diagramNode);
}
}
NOTE
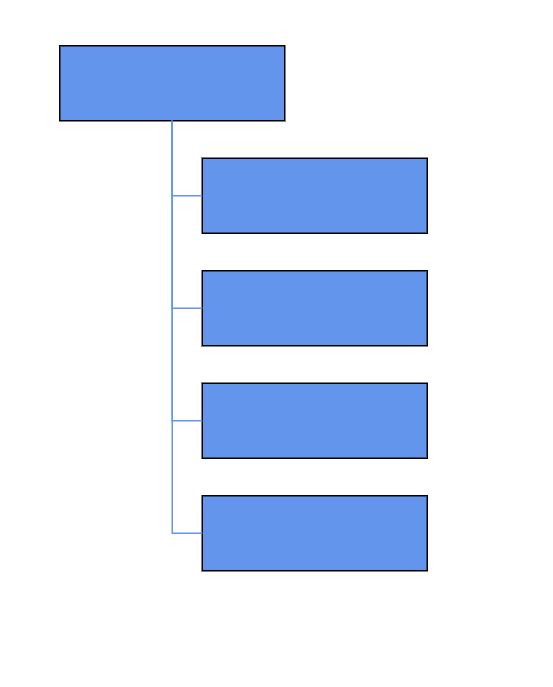
How to Create Organizational Chart
A built-in automatic layout algorithm is designed specifically for organizational charts, automatically arranging parent and child node positions for optimal structure and clarity.
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Inputs
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Diagram
<SfDiagramComponent Height="600px" NodeCreating="@OnNodeCreating" ConnectorCreating="@OnConnectorCreating">
<DataSourceSettings ID="Id" ParentID="Team" DataSource="@DataSource"></DataSourceSettings>
<SnapSettings>
<HorizontalGridLines LineColor="white" LineDashArray="2,2">
</HorizontalGridLines>
<VerticalGridLines LineColor="white" LineDashArray="2,2">
</VerticalGridLines>
</SnapSettings>
<Layout Type="LayoutType.OrganizationalChart" @bind-HorizontalSpacing="@HorizontalSpacing" @bind-VerticalSpacing="@VerticalSpacing" GetLayoutInfo="GetLayoutInfo">
</Layout>
</SfDiagramComponent>
@code
{
//Initializing layout.
int HorizontalSpacing = 40;
int VerticalSpacing = 50;
//To configure every subtree of the organizational chart.
private TreeInfo GetLayoutInfo(IDiagramObject obj, TreeInfo options)
{
options.AlignmentType = SubTreeAlignmentType.Right;
options.Orientation = Orientation.Vertical;
return options;
}
//Creates node with some default values.
private void OnNodeCreating(IDiagramObject obj)
{
Node node = obj as Node;
node.Height = 50;
node.Width = 150;
node.Style = new ShapeStyle() { Fill = "#6495ED", StrokeWidth = 1, StrokeColor = "Black" };
}
//Creates connectors with some default values.
private void OnConnectorCreating(IDiagramObject connector)
{
Connector connectors = connector as Connector;
connectors.Type = ConnectorSegmentType.Orthogonal;
connectors.Style = new TextStyle() { StrokeColor = "#6495ED", StrokeWidth = 1 };
connectors.TargetDecorator = new DecoratorSettings
{
Shape = DecoratorShape.None,
Style = new ShapeStyle() { Fill = "#6495ED", StrokeColor = "#6495ED", }
};
}
public class OrgChartDataModel
{
public string Id { get; set; }
public string Team { get; set; }
public string Role { get; set; }
}
public object DataSource = new List<object>()
{
new OrgChartDataModel() { Id= "1", Role= "General Manager" },
new OrgChartDataModel() { Id= "2", Role= "Human Resource Manager", Team= "1" },
new OrgChartDataModel() { Id= "3", Role= "Design Manager", Team= "1" },
new OrgChartDataModel() { Id= "4", Role= "Operation Manager", Team= "1" },
new OrgChartDataModel() { Id= "5", Role= "Marketing Manager", Team= "1" }
};
}